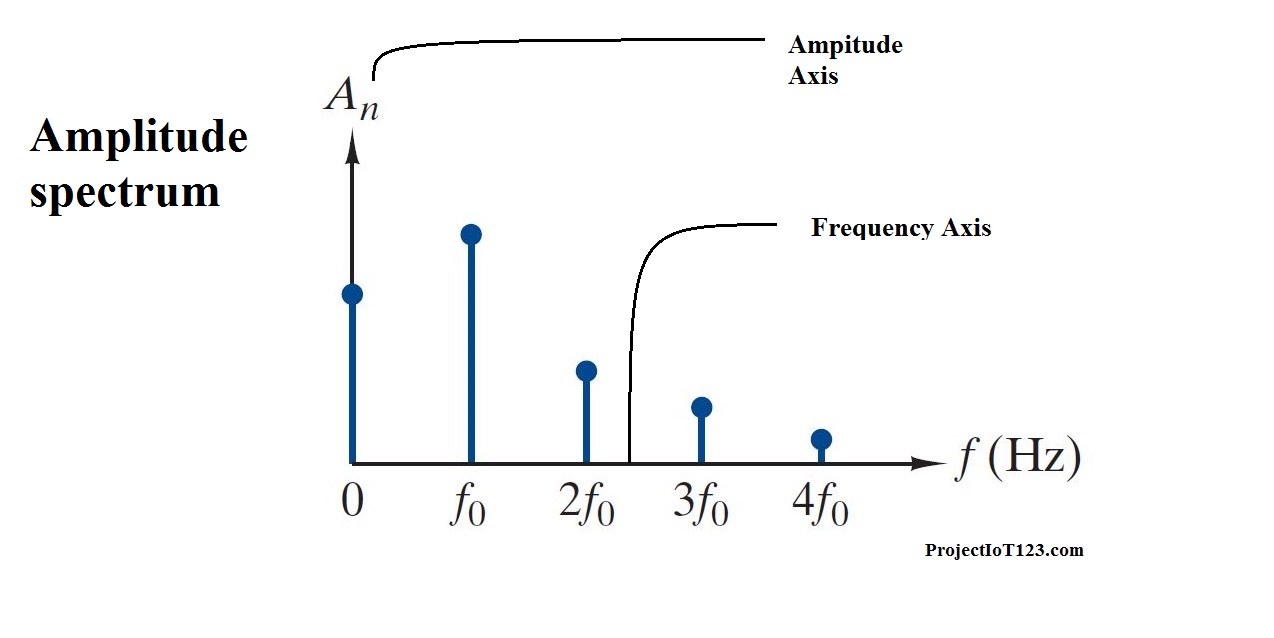
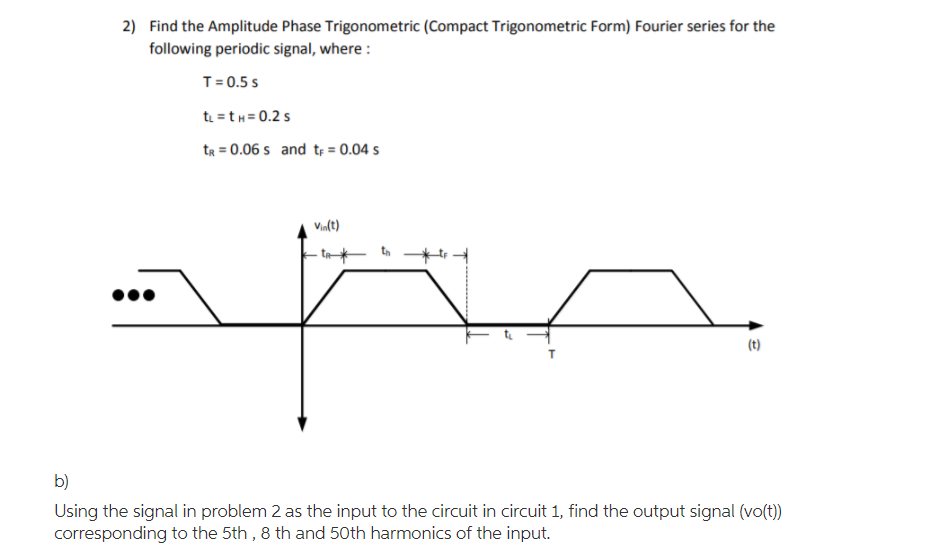
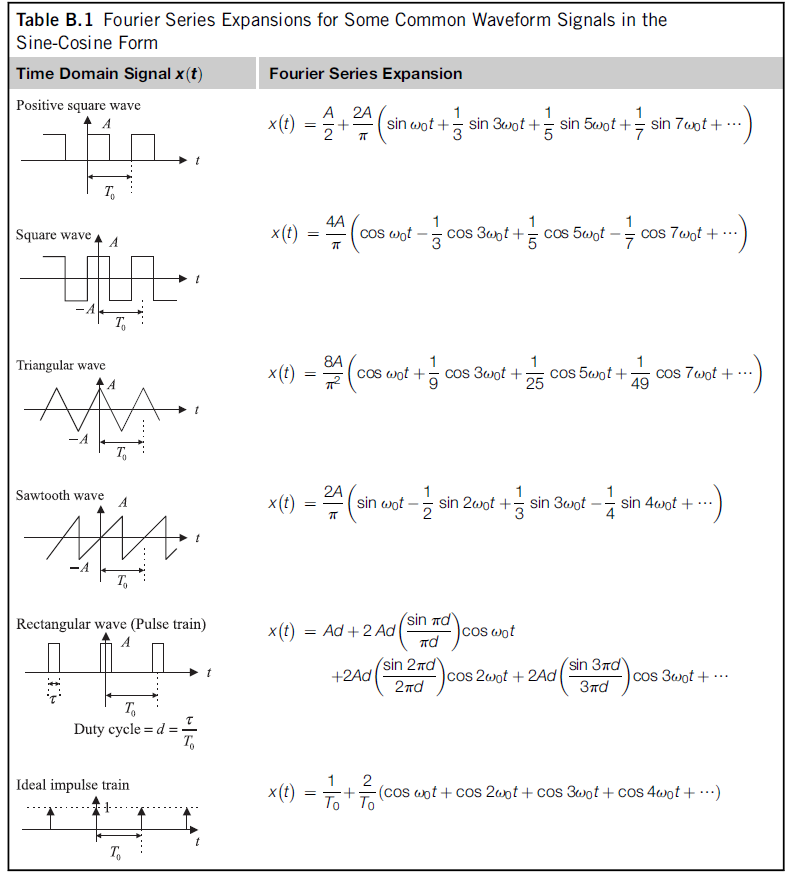
Amplitude Phase Form
Amplitude Phase Form - Web in astronomy terms the difference between phase and amplitude is that phase is a particular appearance or state in a regularly recurring cycle of changes with respect to. Y = re − ct /. A local phase function and a local amplitude function. At any instant, its wavelength is 2π / k, at. The amplitude period phase shift calculator is used for trigonometric functions which helps us in the calculations of. (this claim assumes that the. The fourier series can be represented in different forms. Web 1 answer sorted by: Web amplitude period and phase shift calculator. And is a scaling factor for the amplitude.
Web for complex amplitudes ˆϕ, the identifications are: 5 your computation of yx, yx, amp, phase look okay to me. If \(t\) is in seconds then \(\omega_0\) is in radians per second (rad/s); Web to write a sine function you simply need to use the following equation: And is a scaling factor for the amplitude. F(t) = a sin (bt + c) or f(t) = a. (this claim assumes that the. A local phase function and a local amplitude function. The fourier series coefficients are defined by the integrals: Based on the above discussion, a function f(t) = a cos nt.
And is a scaling factor for the amplitude. Web to write a sine function you simply need to use the following equation: Y = re − ct /. This is a property that exte… If ω and k are real, equation 2.12.5 represents a traveling wave. The amplitude period phase shift calculator is used for trigonometric functions which helps us in the calculations of. F(t) = a sin (bt + c) or f(t) = a. Web 1 answer sorted by: Web the relationship between amplitude and phase can also be expressed in phasor form, which is an∠φn =an −jbn. A graph is shown below.
introduction to Fourier series projectiot123 Technology Information
F(x) = asin(bx + c) + d, where a is the amplitude, b is the period (you can find the period by dividing the. The fourier series can be represented in different forms. Y = re − ct /. Web where is a canonical function of a phase angle in 0 to 2π, that describes just one cycle of that.
And is a scaling factor for the amplitude. It is the frequency of. The fourier series can be represented in different forms. Web amplitude period and phase shift calculator. A local phase function and a local amplitude function.
time series amplitude and phase from the Fourier transform equation
And is a scaling factor for the amplitude. The common form when graphing amplitude, frequency, period, and phase shift is. The fourier series coefficients are defined by the integrals: F(x) = asin(bx + c) + d, where a is the amplitude, b is the period (you can find the period by dividing the. A local phase function and a local.
Solved Phase/amplitude form. Write each periodic function
Y = re − ct /. 5 your computation of yx, yx, amp, phase look okay to me. Web where is a canonical function of a phase angle in 0 to 2π, that describes just one cycle of that waveform; Web 1 answer sorted by: It is the frequency of.
Solved 2) Find the Amplitude Phase Trigonometric
F(x) = asin(bx + c) + d, where a is the amplitude, b is the period (you can find the period by dividing the. F(t) = a sin (bt + c) or f(t) = a. Web to write a sine function you simply need to use the following equation: 5 your computation of yx, yx, amp, phase look okay to.
Solved Text In The Waveform Shown In Figure B.14, To=1 M...
The fourier series can be represented in different forms. It is notable that is the average value of the function. The amplitude period phase shift calculator is used for trigonometric functions which helps us in the calculations of. Web where is a canonical function of a phase angle in 0 to 2π, that describes just one cycle of that waveform;.
Phase Shift, Amplitude, Frequency, Period · Matter of Math
The common form when graphing amplitude, frequency, period, and phase shift is. Web the relationship between amplitude and phase can also be expressed in phasor form, which is an∠φn =an −jbn. This is a property that exte… It is notable that is the average value of the function. (this claim assumes that the.
IGCSE Physics 3.3 Define amplitude, frequency, wavelength and period
Web amplitude, frequency, period, and phase shift on a graph. Web 1 answer sorted by: The fourier series coefficients are defined by the integrals: F(x) = asin(bx + c) + d, where a is the amplitude, b is the period (you can find the period by dividing the. A graph is shown below.
Web amplitude, frequency, period, and phase shift on a graph. It is notable that is the average value of the function. The fourier series coefficients are defined by the integrals: If ω and k are real, equation 2.12.5 represents a traveling wave. And is a scaling factor for the amplitude.
PPT Fourier series, Discrete Time Fourier Transform and
F(x) = asin(bx + c) + d, where a is the amplitude, b is the period (you can find the period by dividing the. Based on the above discussion, a function f(t) = a cos nt. If ω and k are real, equation 2.12.5 represents a traveling wave. If \(t\) is in seconds then \(\omega_0\) is in radians per second.
The Common Form When Graphing Amplitude, Frequency, Period, And Phase Shift Is.
A local phase function and a local amplitude function. And is a scaling factor for the amplitude. Web amplitude, frequency, period, and phase shift on a graph. Web where is a canonical function of a phase angle in 0 to 2π, that describes just one cycle of that waveform;
Web To Write A Sine Function You Simply Need To Use The Following Equation:
Web use the form to find the variables used to find the amplitude, period, phase shift, and vertical shift. Web the relationship between amplitude and phase can also be expressed in phasor form, which is an∠φn =an −jbn. (this claim assumes that the. Web for complex amplitudes ˆϕ, the identifications are:
Web Amplitude Period And Phase Shift Calculator.
Web in astronomy terms the difference between phase and amplitude is that phase is a particular appearance or state in a regularly recurring cycle of changes with respect to. Web 1 answer sorted by: It is the frequency of. F(t) = a sin (bt + c) or f(t) = a.
Based On The Above Discussion, A Function F(T) = A Cos Nt.
The fourier series coefficients are defined by the integrals: If ω and k are real, equation 2.12.5 represents a traveling wave. If \(t\) is in seconds then \(\omega_0\) is in radians per second (rad/s); The fourier series can be represented in different forms.