Ionic Bonds Form Between What Types Of Elements
Ionic Bonds Form Between What Types Of Elements - Because the number of electrons does not equal the number of protons, each ion has a. Ionic bonds result from the attraction between oppositely charged ions. One of the atoms (metal) involved in the bond formation must have a low. Web about 30% of respondents selected all three correctly. Electron transfer produces negative ions called anions and positive ions. Different types of bonds form. Web ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms. Web which elements form ionic bonds? For example, sodium cations (positively charged ions). They form as a result of electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions and usually occur.
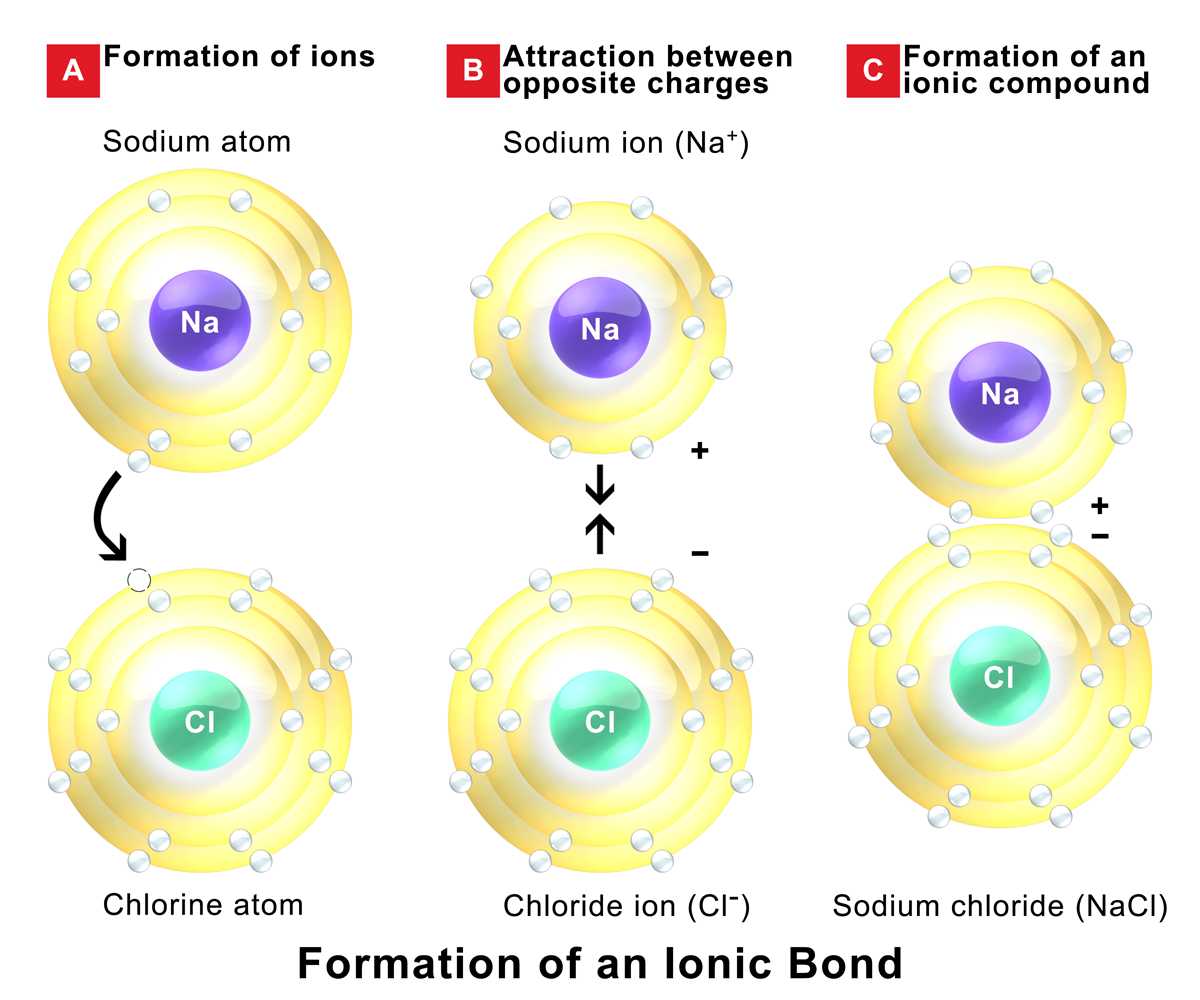
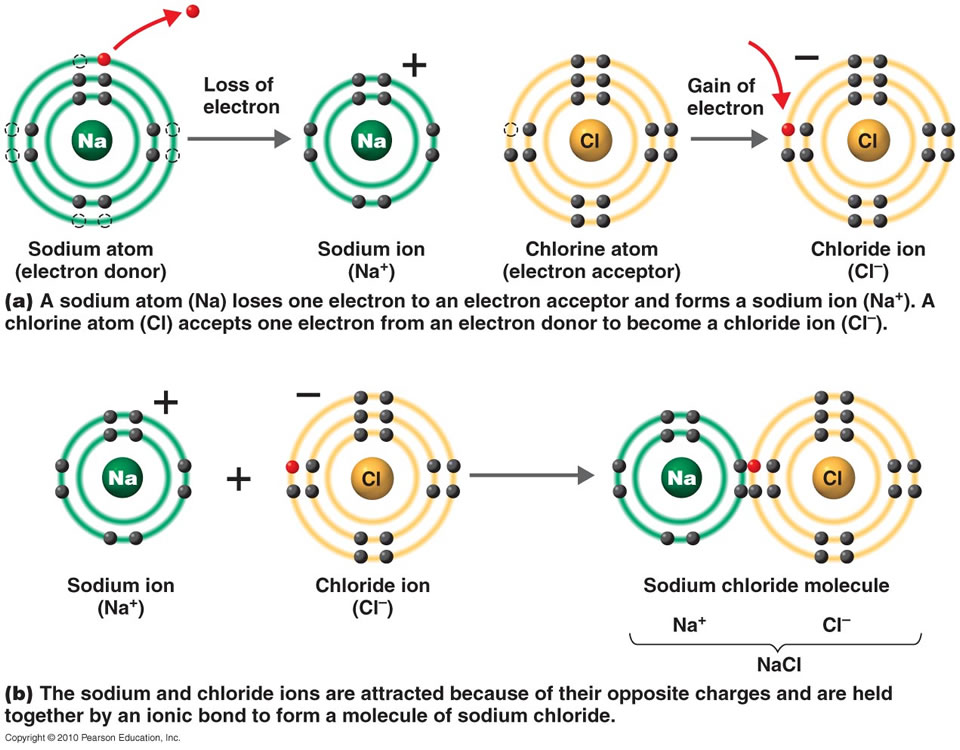
Because the number of electrons does not equal the number of protons, each ion has a. Web when an atom does not contain equal numbers of protons and electrons, it is called an ion. Web one type of chemical bond is an ionic bond. Web ionic bonds form between elements with very different electronegativities, resulting in transfer of electrons between the atoms. Web about 30% of respondents selected all three correctly. Charged chemical species form when neutral atoms, or groups of atoms, lose. A number of students could not “…discriminate between particulate representations of compounds and elements” (p. Web the most common types of elements that form ionic bonds are metals and nonmetals. Web which elements form ionic bonds? Return to bonding menu in modern language, the central idea of an ionic bond is that electrons (one or more, depending on the element).
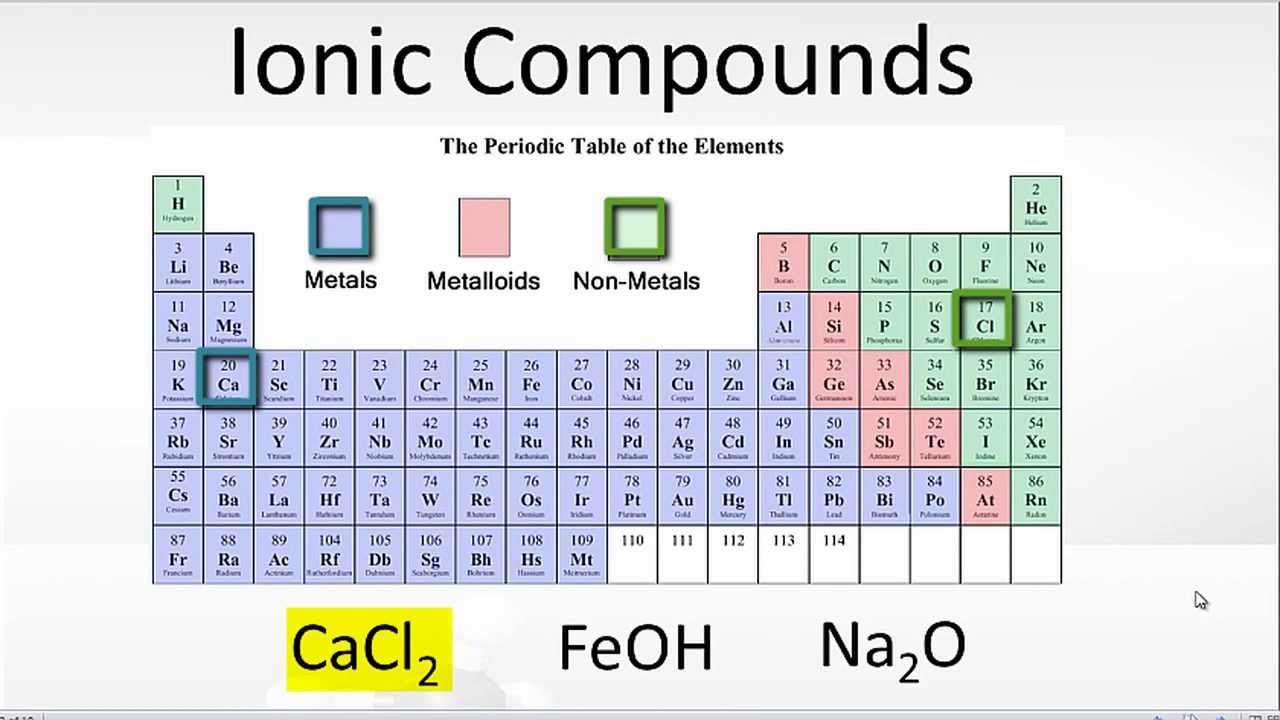
Return to bonding menu in modern language, the central idea of an ionic bond is that electrons (one or more, depending on the element). Transfer of the electrons is energetically. Web the most common types of elements that form ionic bonds are metals and nonmetals. Web ionic bonds form when a nonmetal and a metal exchange electrons, while covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between two nonmetals. Web 1 point if the element lithium (li) were to bond with the element sulfur (s), what type of bond can you predict will be formed and why?* a. Web ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms. Web an ionic bond is a type of chemical bond formed through an electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions. For example, sodium cations (positively charged ions). Ionic bonds are formed between a cation, which. Web which elements form ionic bonds?
Ionic Bond Definition, Types, Properties & Examples
Ionic bonds are formed between a cation, which. Web the most common types of elements that form ionic bonds are metals and nonmetals. Web ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms. Transfer of the electrons is energetically. Web one type of chemical bond is an ionic bond.
savvychemist Ionic Bonding (2) Dot and cross diagrams/Lewis structures
Web an ionic bond is a bond between two oppositively charged chemical species, a cation and an anion. Web one type of chemical bond is an ionic bond. Charged chemical species form when neutral atoms, or groups of atoms, lose. Different types of bonds form. They form as a result of electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions and usually occur.
Examples of Ionic Bonding YouTube
Different types of bonds form. Electron transfer produces negative ions called anions and positive ions. For example, sodium cations (positively charged ions). Ionic bonds are formed between a cation, which. One of the atoms (metal) involved in the bond formation must have a low.
Examples of Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds
Return to bonding menu in modern language, the central idea of an ionic bond is that electrons (one or more, depending on the element). Web one type of chemical bond is an ionic bond. Web an ionic bond is a type of chemical bond formed through an electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions. Web ionic bonds are one of.
How Does An Ionic Bond Form Between Sodium And Chlorine slideshare
For example, sodium cations (positively charged ions). Web one type of chemical bond is an ionic bond. They form as a result of electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions and usually occur. Web which elements form ionic bonds? Because the number of electrons does not equal the number of protons, each ion has a.
Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules The Building Blocks · Biology
Web the most common types of elements that form ionic bonds are metals and nonmetals. Electron transfer produces negative ions called anions and positive ions. Web ionic bonds form when a nonmetal and a metal exchange electrons, while covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between two nonmetals. Web when an atom does not contain equal numbers of protons and.
Ionic Properties
Web an ionic bond is a bond between two oppositively charged chemical species, a cation and an anion. Web ionic bonds form when a nonmetal and a metal exchange electrons, while covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between two nonmetals. Web which elements form ionic bonds? Return to bonding menu in modern language, the central idea of an ionic.
Ionic Bond Definition, Types, Properties & Examples
Return to bonding menu in modern language, the central idea of an ionic bond is that electrons (one or more, depending on the element). Charged chemical species form when neutral atoms, or groups of atoms, lose. Ionic bonds result from the attraction between oppositely charged ions. Web 1 point if the element lithium (li) were to bond with the element.
Ionic Bond Definition, Types, Properties & Examples
Web one type of chemical bond is an ionic bond. For example, sodium cations (positively charged ions). Web ionic bonds form when a nonmetal and a metal exchange electrons, while covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between two nonmetals. Web ionic bonds form between elements with very different electronegativities, resulting in transfer of electrons between the atoms. Web which.
Ionic Compounds Ionic bonds, Properties, Formation, Examples, Videos
Web when an atom does not contain equal numbers of protons and electrons, it is called an ion. Because the number of electrons does not equal the number of protons, each ion has a. Web ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms. Different types of bonds form. One of.
Web The Most Common Types Of Elements That Form Ionic Bonds Are Metals And Nonmetals.
Different types of bonds form. Web ionic bonds form when a nonmetal and a metal exchange electrons, while covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between two nonmetals. Web ionic bonds are one of the two main types of chemical bonds. Web when an atom does not contain equal numbers of protons and electrons, it is called an ion.
Web Ionic Bonds Form Between Elements With Very Different Electronegativities, Resulting In Transfer Of Electrons Between The Atoms.
Web about 30% of respondents selected all three correctly. Web one type of chemical bond is an ionic bond. A number of students could not “…discriminate between particulate representations of compounds and elements” (p. Web which elements form ionic bonds?
Because The Number Of Electrons Does Not Equal The Number Of Protons, Each Ion Has A.
For example, sodium cations (positively charged ions). They form as a result of electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions and usually occur. Web an ionic bond is a bond between two oppositively charged chemical species, a cation and an anion. Web ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms.
Ionic Bonds Result From The Attraction Between Oppositely Charged Ions.
Electron transfer produces negative ions called anions and positive ions. Charged chemical species form when neutral atoms, or groups of atoms, lose. Web 1 point if the element lithium (li) were to bond with the element sulfur (s), what type of bond can you predict will be formed and why?* a. Ionic bonds are formed between a cation, which.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ionic-bond-58fd4ea73df78ca1590682ad.jpg)
.PNG)