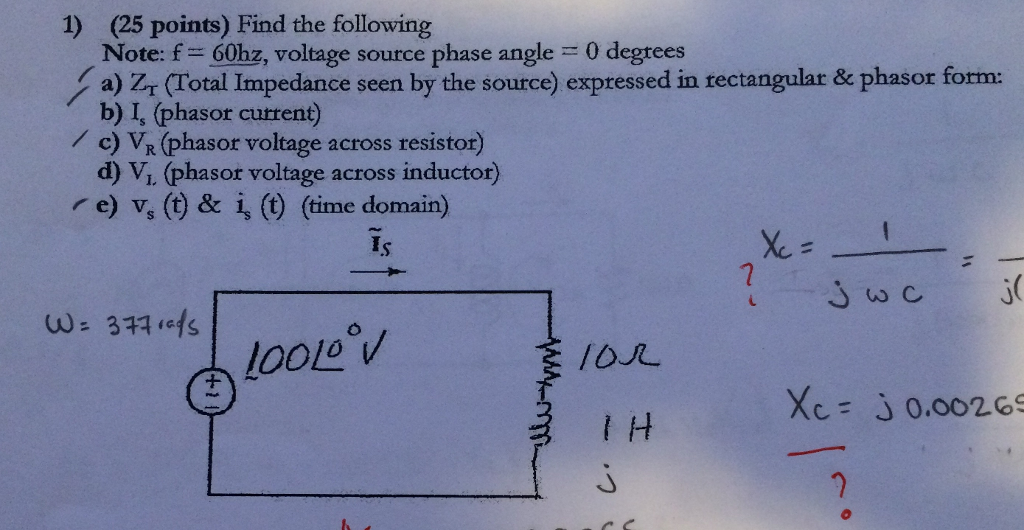Phasor Form To Rectangular Form
Phasor Form To Rectangular Form - My textbook defines phasors as $$v(t) = v_m\text{cos}(\omega t + \phi) = \text{re}[v_me^{j(\omega t + \phi)} ]$$ Web remember, there are 3 forms to phasors : Converting between forms when working with phasors it is often necessary to convert between rectangular and polar form. To multiply together two vectors in polar form, we must first multiply together the two modulus or magnitudes and then add together their angles. Why the second phasor is been expressed as a sin function. Web phasor and exponential forms are identical and are also referred to as polar form. Rectangular, polar or exponential form. Phasor form rectangular form exponential form phasor and exponential forms are identical and are also referred to as polar form. Addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, squaring, square root,. Thus, phasor notation defines the effective (rms) magnitude of voltages and currents.
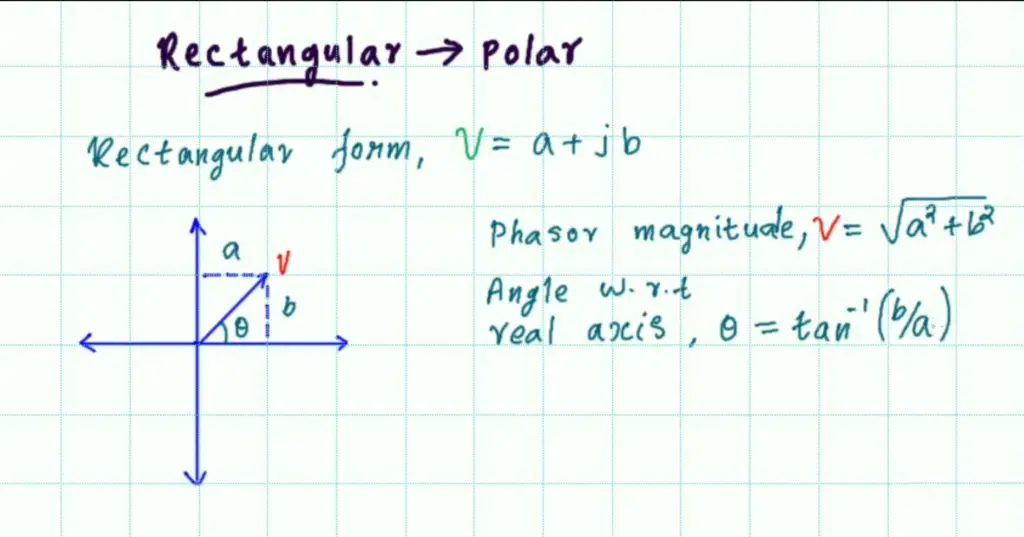
Web phasor calculator * general instructions and information * convert phasor from rectangular to polar form * convert phasor from polar to rectangular form The polar form is represented by vector magnitude and angle with respect to the. Rectangular, polar or exponential form. Convert an impedance in rectangular (complex) form z = 5 + j 2 ω to polar form. My textbook defines phasors as $$v(t) = v_m\text{cos}(\omega t + \phi) = \text{re}[v_me^{j(\omega t + \phi)} ]$$ Converting between forms when working with phasors it is often necessary to convert between rectangular and polar form. Web 9.5k views 6 years ago. This is all based off the fact that the polar form takes on the format, amplitude < phase. Let z be the phasor quantity. To convert from rectangular form to polar form:
Web phasor calculator * general instructions and information * convert phasor from rectangular to polar form * convert phasor from polar to rectangular form The rectangular form is represented by a real part (horizontal axis) and an imaginary (vertical axis) part of the vector. The method of conversion of polar form to a rectangular form is shown in this video. Phasor form rectangular form exponential form phasor and exponential forms are identical and are also referred to as polar form. For example, (a + jb). Web the complex numbers in rectangular form plotted in fig.a.1 may now be converted to exponential form (or polar form): To convert from rectangular form to polar form: Web rectangular form is best for adding and subtracting complex numbers as we saw above, but polar form is often better for multiplying and dividing. Thus, phasor notation defines the effective (rms) magnitude of voltages and currents. R = x 2 + y 2 r = ( − 3) 2 + 4 2 r = 5 the phase angle is defined as:
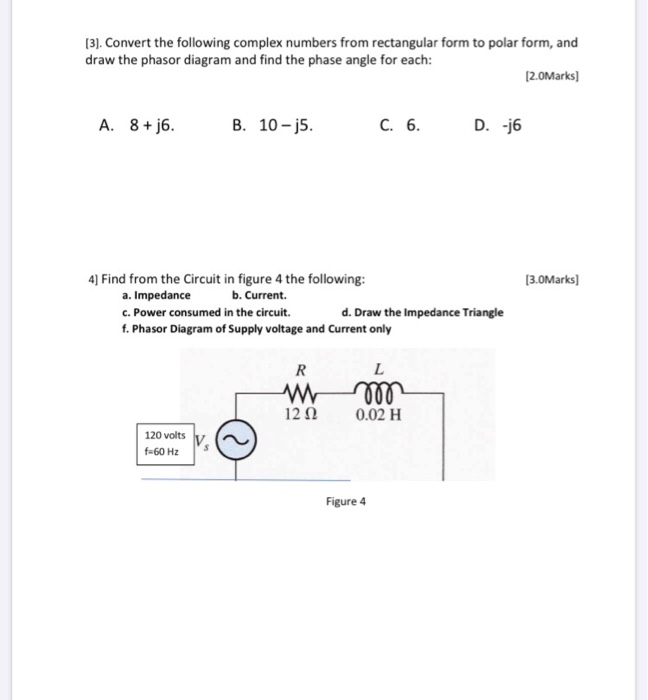
Solved (3). Convert the following complex numbers from
Second, click convert button to calculate polar terms. This is all based off the fact that the polar form takes on the format, amplitude < phase. Click convert button to calculate real and imaginary terms. Web phasor calculator * general instructions and information * convert phasor from rectangular to polar form * convert phasor from polar to rectangular form Web.
Rectangular to Polar form & Polar to Rectangular form conversion
Web phasor calculator * general instructions and information * convert phasor from rectangular to polar form * convert phasor from polar to rectangular form The rectangular form is represented by a real part (horizontal axis) and an imaginary (vertical axis) part of the vector. When working with phasors it is often necessary to convert between rectangular and polar form. R.
ac Obtaining sinusoidal expression Electrical Engineering Stack
Phasor form rectangular form exponential form phasor and exponential forms are identical and are also referred to as polar form. Yagle, eecs 206 instructor, fall 2005 dept. This is all based off the fact that the polar form takes on the format, amplitude < phase. Web i can get the answer: The polar form is represented by vector magnitude and.
Rectangular to Polar form & Polar to Rectangular form conversion
Φ = t a n − 1 ( y x) our reference angle will be: When working with phasors it is often necessary to convert between rectangular and polar form. To convert from rectangular form to polar form: The rectangular form is represented by a real part (horizontal axis) and an imaginary (vertical axis) part of the vector. Web v.
Web 9.5k views 6 years ago. Web v = − 3 + j 4 we will first convert the phasor from rectangular form to exponential form. Web rectangular form is best for adding and subtracting complex numbers as we saw above, but polar form is often better for multiplying and dividing. This calculator performs the following arithmetic operation on complex.
Phasor representation YouTube
Web rectangular form is best for adding and subtracting complex numbers as we saw above, but polar form is often better for multiplying and dividing. There's also a graph which shows you the meaning of what you've found. An instantaneous quantity described simply in terms of vector angle and length is called polar form, for example 1 volt \(\angle\) 67.5\(^{o..
Phasor Diagram OER
Click convert button to calculate real and imaginary terms. = + = to convert from polar to rectangular form: Second, click convert button to calculate polar terms. Web 15k views 5 years ago. In this video, shows a method to convert the rectangular form to a polar form.
Solved Find Zt (Total Impedance seen by the source)
A rectangular form is a complex number represented by horizontal and vertical components. The polar form is represented by vector magnitude and angle with respect to the. The rectangular form is represented by a real part (horizontal axis) and an imaginary (vertical axis) part of the vector. Convert real part not computed imaginary part not computed To convert from rectangular.
Polar to rectangular form conversion Phasor form conversions YouTube
First, enter real and imaginary values: Web for detailed understanding of the concept, learn the mathematical representation of phasor in complex form. There's also a graph which shows you the meaning of what you've found. Rectangular, polar or exponential form. Web 15k views 5 years ago.
Electrical Systems Operators j and a in Electrical Engineering
To convert from rectangular form to polar. Convert a voltage in polar form u = 206 ∠120° v to. Web an instantaneous quantity (e.g. Thus, phasor notation defines the effective (rms) magnitude of voltages and currents. Web phasor calculator * general instructions and information * convert phasor from rectangular to polar form * convert phasor from polar to rectangular form
Web An Instantaneous Quantity (E.g.
Web polar forms of numbers can be converted into their rectangular equivalents by the formula, rectangular form= amplitude * cos (phase) + j (amplitude) * sin (phase). A rectangular form is a complex number represented by horizontal and vertical components. Web i'm doing an assignment on circuit analysis with phasors and it's brought up a point of confusion for me on how phasors convert to rectangular form. Rectangular, polar or exponential form.
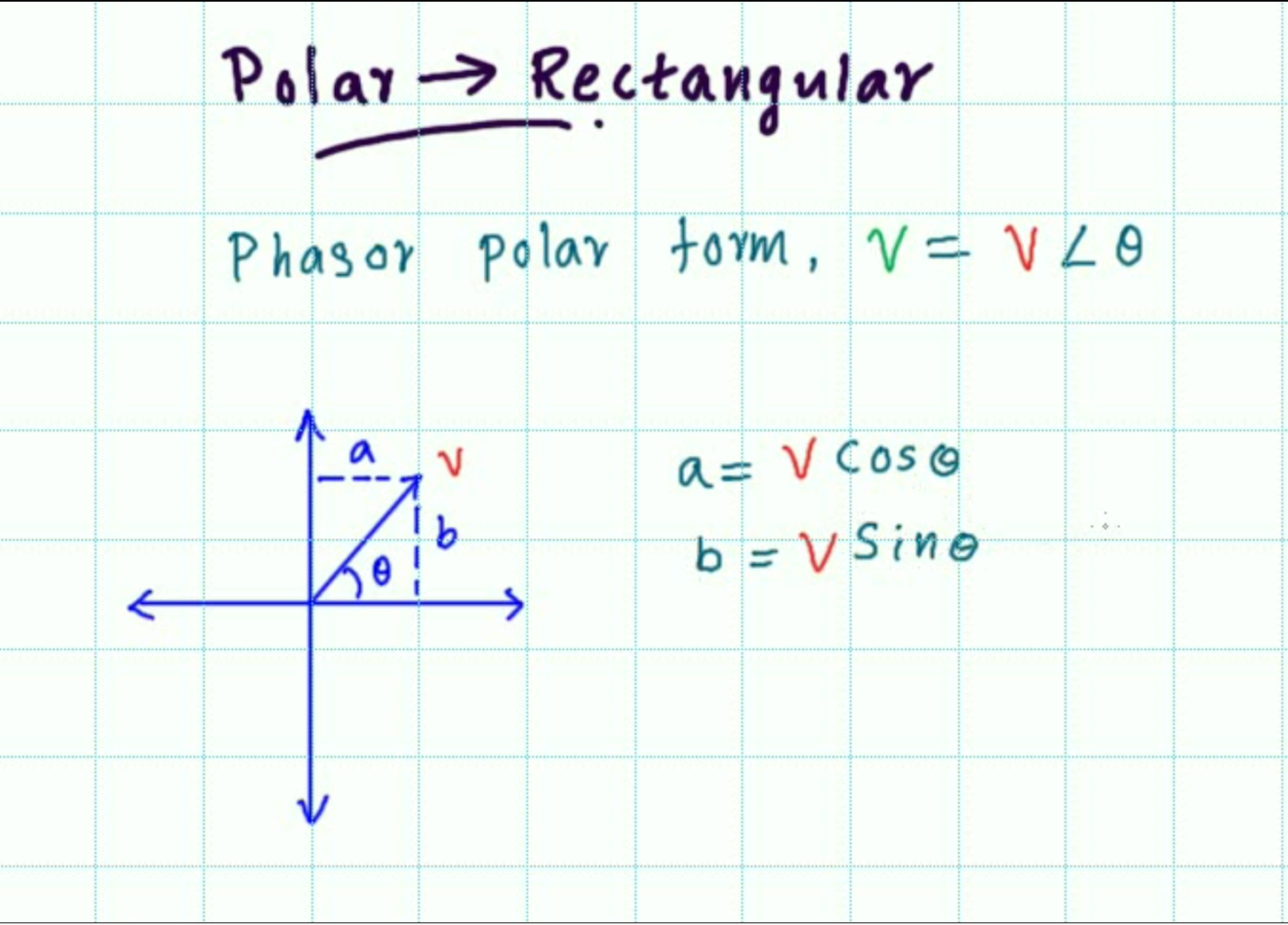
Converting Between Forms When Working With Phasors It Is Often Necessary To Convert Between Rectangular And Polar Form.
Φ = t a n − 1 ( y x) our reference angle will be: An instantaneous quantity described simply in terms of vector angle and length is called polar form, for example 1 volt \(\angle\) 67.5\(^{o. The rectangular form is represented by a real part (horizontal axis) and an imaginary (vertical axis) part of the vector. Convert real part not computed imaginary part not computed
There's Also A Graph Which Shows You The Meaning Of What You've Found.
Voltage or current at some moment in time) described simply in terms of real and imaginary values is called rectangular form, for example 0.3827 + \(j\)0.9239 volts. What i don't understand is: My textbook defines phasors as $$v(t) = v_m\text{cos}(\omega t + \phi) = \text{re}[v_me^{j(\omega t + \phi)} ]$$ It is converted into polar form, represented as z = e ∠± ϕ.
Polar Form Is A Complex Number Is Denoted By Its Absolute Value And The Angle Of Its Vector.
Web for detailed understanding of the concept, learn the mathematical representation of phasor in complex form. The method of conversion of polar form to a rectangular form is shown in this video. Why the second phasor is been expressed as a sin function. The polar form is represented by vector magnitude and angle with respect to the.