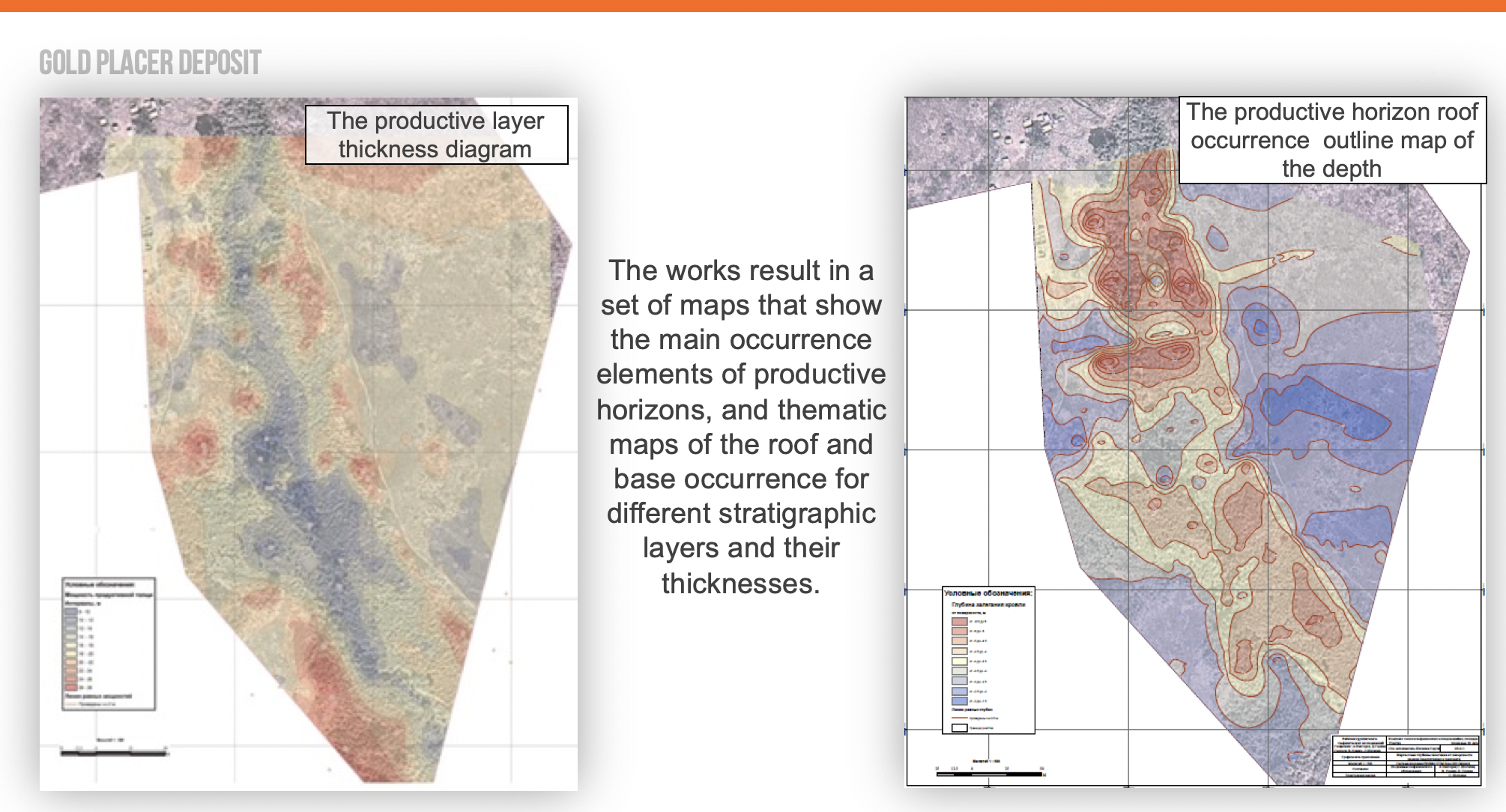
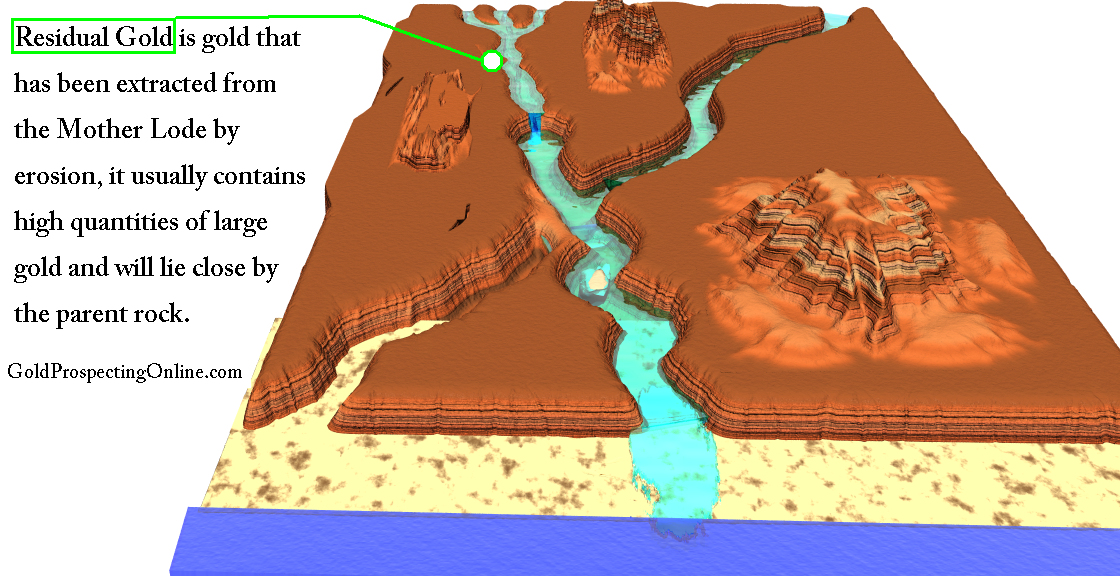
Placer Deposits Form When
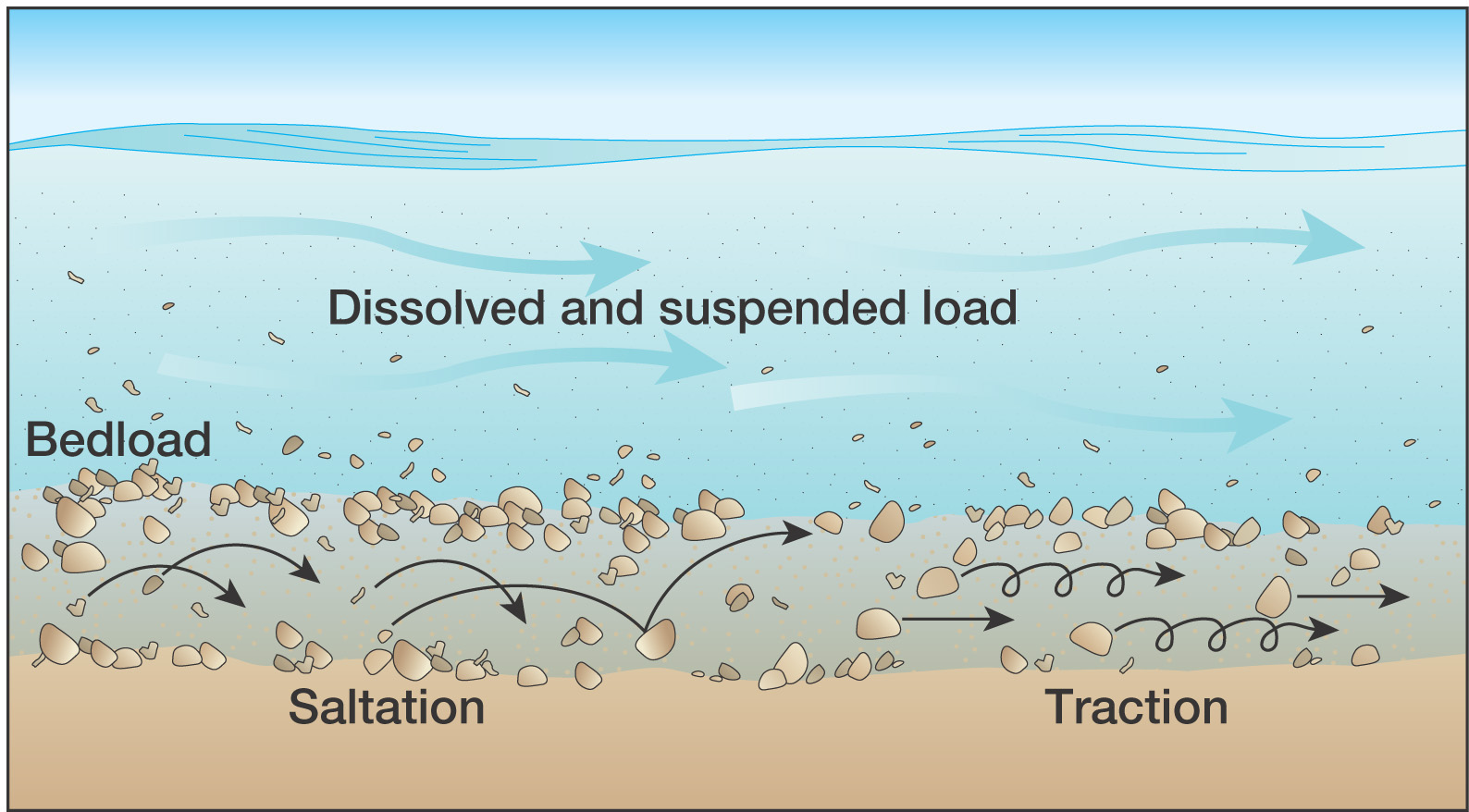
Placer Deposits Form When - Unless preserved by burial, a placer subsequently may be eroded, and either dispersed or reconcentrated. Placer deposits naturally accumulate heavy, valuable minerals, which are formed by the gravitational effect during sedimentary processes. When heavy, stable minerals are freed from their matrix by weathering processes, they are slowly washed downslope into. Placer mining is frequently used for precious metal deposits (particularly gold) and gemstones, both of which are. Placers can be found in rivers (alluvial placers) and on the coast, particularly in beaches. Mineral deposits formed as a result of gravity separation based on density are called placer deposits. Web placer mining ( / ˈplæsər /) [1] is the mining of stream bed ( alluvial) deposits for minerals. Web so, placer deposits, also just called placers, form when one or more minerals concentrate in this way to become an ore deposit. Web “placer” deposits are formed by surface weathering and ocean, river or wind action resulting in concentration of some valuable heavy resistant minerals of economic quantities. Placer deposits form when heavy eroded particles settle out of moving water.
Web “placer” deposits are formed by surface weathering and ocean, river or wind action resulting in concentration of some valuable heavy resistant minerals of economic quantities. The name is from the spanish word placer , meaning alluvial sand. The word placer is spanish for alluvial sand. Placer deposits form when heavy eroded particles settle out of moving water. Web placer deposits result from weathering and release of gold from lode deposits, transportation of the gold, and concentration of the gold dominantly in stream gravels. The placer can be an accumulation of valuable minerals formed by gravity separation during sedimentary processes. Heavy eroded particles settle out of moving water. Unless preserved by burial, a placer subsequently may be eroded, and either dispersed or reconcentrated. Web placer mining ( / ˈplæsər /) [1] is the mining of stream bed ( alluvial) deposits for minerals. Minerals that form placer deposits include precious deposits like gold, platinum, copper, zircon and various gemstones apart from magnetite, ilmenite, chromite, cassiterite, rutile, and native monazite.
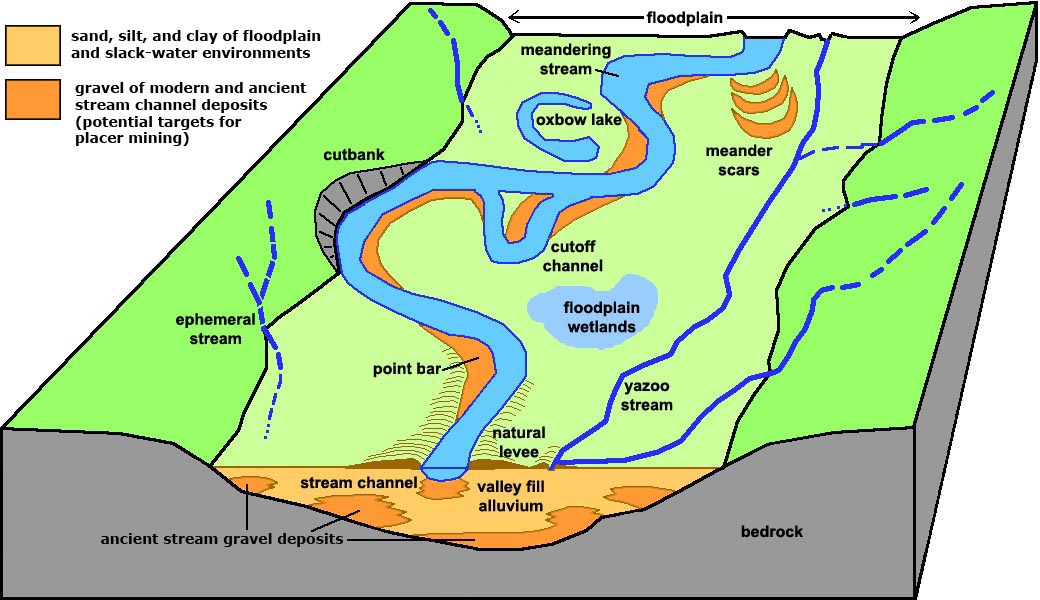
Mineral deposits formed as a result of gravity separation based on density are called placer deposits. Minerals that form placer deposits include precious deposits like gold, platinum, copper, zircon and various gemstones apart from magnetite, ilmenite, chromite, cassiterite, rutile, and native monazite. Typically, placers form where a stream’s velocity slows on point bars, in braided streams, or in alluvial fans (figure 9.92). Web “placer” deposits are formed by surface weathering and ocean, river or wind action resulting in concentration of some valuable heavy resistant minerals of economic quantities. Web in geology, a placer deposit or placer is an accumulation of valuable minerals formed by gravity separation from a specific source rock during sedimentary processes. Unless preserved by burial, a placer subsequently may be eroded, and either dispersed or reconcentrated. Web placer mining ( / ˈplæsər /) [1] is the mining of stream bed ( alluvial) deposits for minerals. Placer mining is frequently used for precious metal deposits (particularly gold) and gemstones, both of which are. Web a placer is any waterborne deposit of sand or gravel that contains concentrated grains of valuable minerals such as gold or magnetite, grains that had originally been eroded from bedrock but were then transported and concentrated by the flowing water. The word placer is spanish for alluvial sand.
Model of Ore Deposits Mining Geology
Web mineral found in placer deposits. Heavy eroded particles settle out of moving water. Placer mining is frequently used for precious metal deposits (particularly gold) and gemstones, both of which are. The name is from the spanish word placer , meaning alluvial sand. Unless preserved by burial, a placer subsequently may be eroded, and either dispersed or reconcentrated.
PLACER TYPE DEPOSITS
Web a placer is any waterborne deposit of sand or gravel that contains concentrated grains of valuable minerals such as gold or magnetite, grains that had originally been eroded from bedrock but were then transported and concentrated by the flowing water. When heavy, stable minerals are freed from their matrix by weathering processes, they are slowly washed downslope into. Unless.
Gold Placer Deposits Stock Image F031/4026 Science Photo Library
Web placer deposits result from weathering and release of gold from lode deposits, transportation of the gold, and concentration of the gold dominantly in stream gravels. When heavy, stable minerals are freed from their matrix by weathering processes, they are slowly washed downslope into. Heavy eroded particles settle out of moving water. Web placer deposit, natural concentration of heavy minerals.
Placer deposits form when ____. (1 point) hot, metalrich fluids cool
Placer deposits form when heavy eroded particles settle out of moving water. The placer can be an accumulation of valuable minerals formed by gravity separation during sedimentary processes. The name is from the spanish word placer , meaning alluvial sand. Web in geology, a placer deposit or placer is an accumulation of valuable minerals formed by gravity separation from a.
SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS X REVISION PAPER TRIVIA AND VISUAL
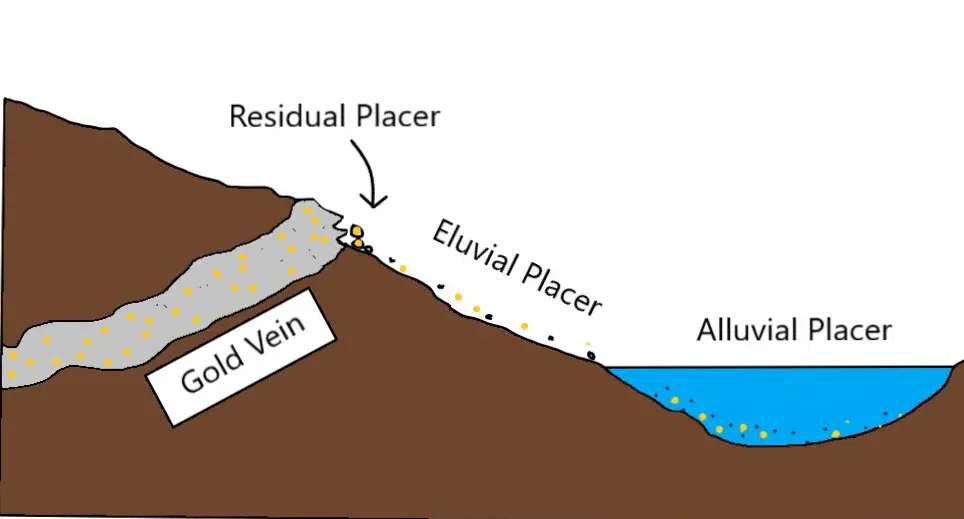
Placers can be found in rivers (alluvial placers) and on the coast, particularly in beaches. The placer can be an accumulation of valuable minerals formed by gravity separation during sedimentary processes. The word placer is spanish for alluvial sand. Web a placer is any waterborne deposit of sand or gravel that contains concentrated grains of valuable minerals such as gold.
Cuántas transmisiones es oro? startupassembly.co
Web in geology, a placer deposit or placer is an accumulation of valuable minerals formed by gravity separation from a specific source rock during sedimentary processes. When heavy, stable minerals are freed from their matrix by weathering processes, they are slowly washed downslope into. The word placer is spanish for alluvial sand. Web placer deposits result from weathering and release.
Tin Deposits in Indonesia SEG UGMSC
The name is from the spanish word placer , meaning alluvial sand. Web a placer is any waterborne deposit of sand or gravel that contains concentrated grains of valuable minerals such as gold or magnetite, grains that had originally been eroded from bedrock but were then transported and concentrated by the flowing water. Minerals that form placer deposits include precious.
(PDF) Placer Mineral Deposits
Web placer deposit, natural concentration of heavy minerals caused by the effect of gravity on moving particles. Web placer deposits result from weathering and release of gold from lode deposits, transportation of the gold, and concentration of the gold dominantly in stream gravels. The word placer is spanish for alluvial sand. Web so, placer deposits, also just called placers, form.
Where Does Placer Gold Come From? Part 3 Placer West Coast Placer
Typically, placers form where a stream’s velocity slows on point bars, in braided streams, or in alluvial fans (figure 9.92). The placer can be an accumulation of valuable minerals formed by gravity separation during sedimentary processes. Web mineral found in placer deposits. The name is from the spanish word placer , meaning alluvial sand. Web placer deposit, natural concentration of.
Types of Placers
The word placer is spanish for alluvial sand. Web placer mining ( / ˈplæsər /) [1] is the mining of stream bed ( alluvial) deposits for minerals. Web in geology, a placer deposit or placer is an accumulation of valuable minerals formed by gravity separation from a specific source rock during sedimentary processes. Web mineral found in placer deposits. Web.
Typically, Placers Form Where A Stream’s Velocity Slows On Point Bars, In Braided Streams, Or In Alluvial Fans (Figure 9.92).
Placer deposits form when heavy eroded particles settle out of moving water. Placer deposits naturally accumulate heavy, valuable minerals, which are formed by the gravitational effect during sedimentary processes. The placer can be an accumulation of valuable minerals formed by gravity separation during sedimentary processes. Placers can be found in rivers (alluvial placers) and on the coast, particularly in beaches.
Web Placer Deposit, Natural Concentration Of Heavy Minerals Caused By The Effect Of Gravity On Moving Particles.
Placer mining is frequently used for precious metal deposits (particularly gold) and gemstones, both of which are. Web placer mining ( / ˈplæsər /) [1] is the mining of stream bed ( alluvial) deposits for minerals. Web “placer” deposits are formed by surface weathering and ocean, river or wind action resulting in concentration of some valuable heavy resistant minerals of economic quantities. Web so, placer deposits, also just called placers, form when one or more minerals concentrate in this way to become an ore deposit.
Web A Placer Is Any Waterborne Deposit Of Sand Or Gravel That Contains Concentrated Grains Of Valuable Minerals Such As Gold Or Magnetite, Grains That Had Originally Been Eroded From Bedrock But Were Then Transported And Concentrated By The Flowing Water.
When heavy, stable minerals are freed from their matrix by weathering processes, they are slowly washed downslope into. Web mineral found in placer deposits. Heavy eroded particles settle out of moving water. Unless preserved by burial, a placer subsequently may be eroded, and either dispersed or reconcentrated.
Web In Geology, A Placer Deposit Or Placer Is An Accumulation Of Valuable Minerals Formed By Gravity Separation From A Specific Source Rock During Sedimentary Processes.
The name is from the spanish word placer , meaning alluvial sand. The word placer is spanish for alluvial sand. Mineral deposits formed as a result of gravity separation based on density are called placer deposits. Web placer deposits result from weathering and release of gold from lode deposits, transportation of the gold, and concentration of the gold dominantly in stream gravels.