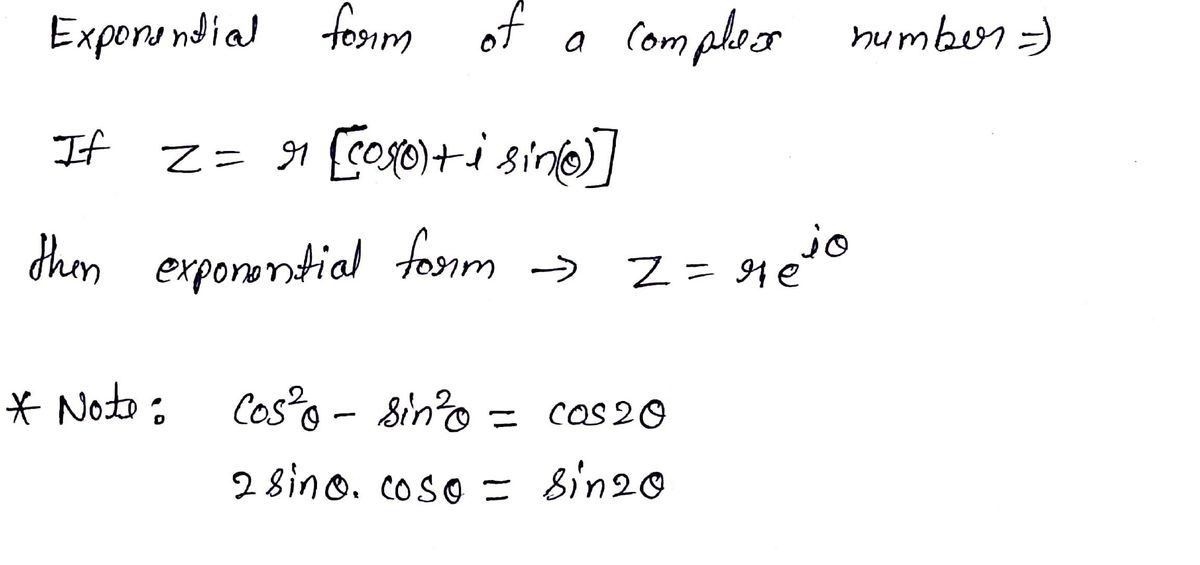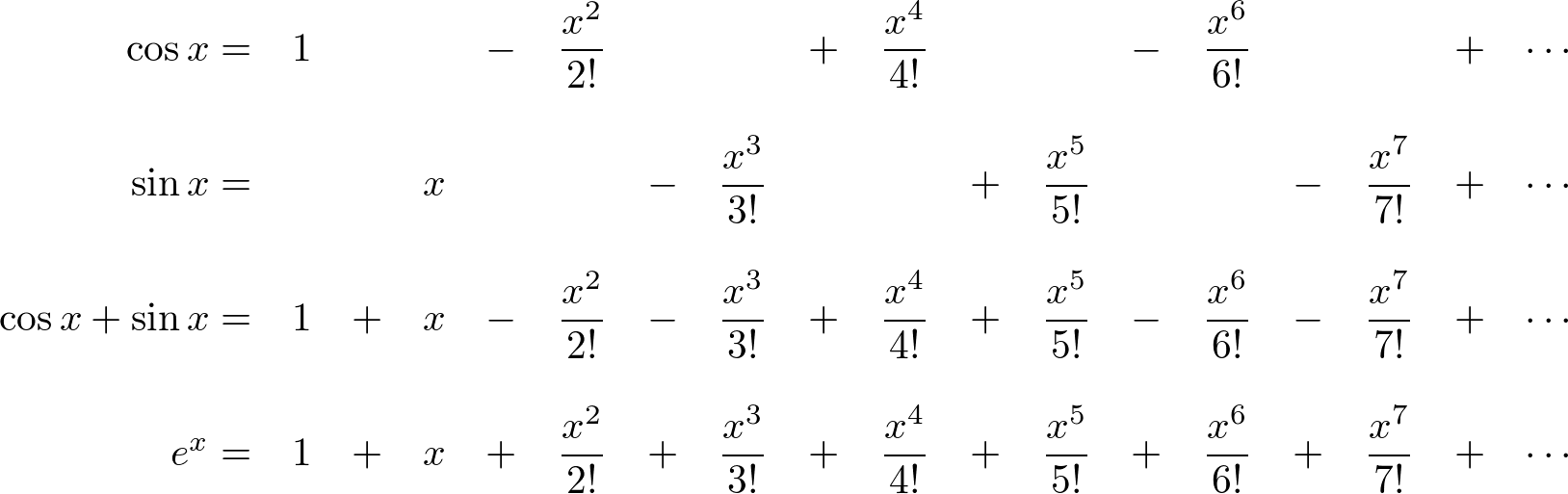Sin In Exponential Form
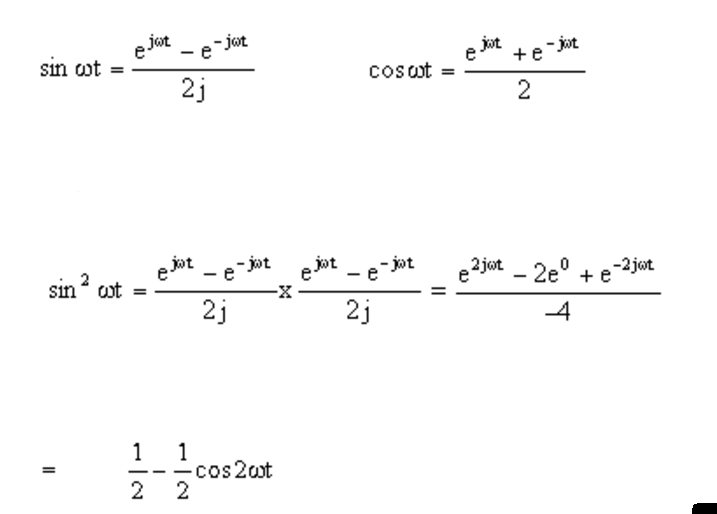
Sin In Exponential Form - If μ r then eiμ def = cos μ + i sin μ. Periodicity of the imaginary exponential. Web start with the definitions of the hyperbolic sine and cosine functions: E jx = cos (x) + jsin (x) and the exponential representations of sin & cos, which are derived from euler's formula: Eit = cos t + i. Sinz denotes the complex sine function. Web solving this linear system in sine and cosine, one can express them in terms of the exponential function: Web hyperbolic functions in mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions, but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circle. I tried using eulers identity to reduce all sine. Sin x = e i x − e − i x 2 i cos x = e i x + e − i x 2.
Web an exponential equation is an equation that contains an exponential expression of the form b^x, where b is a constant (called the base) and x is a variable. Web hyperbolic functions in mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions, but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circle. Web spring 2003 notes on the complex exponential and sine functions (x1.5) i. Web according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and sin(t) via the following inspired definition: If μ r then eiμ def = cos μ + i sin μ. Periodicity of the imaginary exponential. What is going on, is that electrical engineers tend to ignore the fact that one needs to add or subtract the complex. Expz denotes the exponential function. Web start with the definitions of the hyperbolic sine and cosine functions: Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions.
Periodicity of the imaginary exponential. A) sin(x + y) = sin(x)cos(y) + cos(x)sin(y) and. Eit = cos t + i. Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions. Web hyperbolic functions in mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions, but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circle. Web spring 2003 notes on the complex exponential and sine functions (x1.5) i. Web start with the definitions of the hyperbolic sine and cosine functions: Web the exponential form of a complex number using the polar form, a complex number with modulus r and argument θ may be written = r(cos θ + j sin θ) it follows immediately from. Sin x = e i x − e − i x 2 i cos x = e i x + e − i x 2. Web an exponential equation is an equation that contains an exponential expression of the form b^x, where b is a constant (called the base) and x is a variable.
EM to Optics 10 Converting Cos & Sine to Complex Exponentials YouTube
For any complex number z : Eit = cos t + i. Periodicity of the imaginary exponential. I tried using eulers identity to reduce all sine. (45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all.
Answered Express (cos(20)+i sin(20))*in… bartleby
Web the exponential form of a complex number using the polar form, a complex number with modulus r and argument θ may be written = r(cos θ + j sin θ) it follows immediately from. (45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all. Web according to euler, we should regard the.
Question Video Converting the Product of Complex Numbers in Polar Form
For any complex number z : What is going on, is that electrical engineers tend to ignore the fact that one needs to add or subtract the complex. Web solving this linear system in sine and cosine, one can express them in terms of the exponential function: Sinz denotes the complex sine function. Web the exponential form of a complex.
Particular solution for sin using complex exponentials YouTube
For any complex number z : Sinz denotes the complex sine function. Web spring 2003 notes on the complex exponential and sine functions (x1.5) i. Web solving this linear system in sine and cosine, one can express them in terms of the exponential function: Eit = cos t + i.
voltage How to convert sine to exponential form? Electrical
Periodicity of the imaginary exponential. Web hyperbolic functions in mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions, but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circle. Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions. What is going on, is that electrical engineers tend to ignore the fact that one needs to add or subtract the complex. Sin .
Euler's Equation
Web an exponential equation is an equation that contains an exponential expression of the form b^x, where b is a constant (called the base) and x is a variable. I tried using eulers identity to reduce all sine. (45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all. Eit = cos t +.
Example 10 Write exponential form for 8 x 8 x 8 x 8 taking base as 2
Sinz denotes the complex sine function. Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions. Expz denotes the exponential function. I tried using eulers identity to reduce all sine. Web using the exponential forms of cos(theta) and sin(theta) given in (3.11a, b), prove the following trigonometric identities:
Basics of QPSK modulation and display of QPSK signals Electrical
Web start with the definitions of the hyperbolic sine and cosine functions: A) sin(x + y) = sin(x)cos(y) + cos(x)sin(y) and. Eit = cos t + i. E jx = cos (x) + jsin (x) and the exponential representations of sin & cos, which are derived from euler's formula: Web using the exponential forms of cos(theta) and sin(theta) given in.
Other Math Archive January 29, 2018
Sinz denotes the complex sine function. Web according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and sin(t) via the following inspired definition: Expz denotes the exponential function. (45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all. Web start with the definitions of the.
Exponents lesson 4 numbers in exponential form raised to a power
What is going on, is that electrical engineers tend to ignore the fact that one needs to add or subtract the complex. Web spring 2003 notes on the complex exponential and sine functions (x1.5) i. For any complex number z : Web the exponential form of a complex number using the polar form, a complex number with modulus r and.
Web The Exponential Form Of A Complex Number Using The Polar Form, A Complex Number With Modulus R And Argument Θ May Be Written = R(Cos Θ + J Sin Θ) It Follows Immediately From.
Expz denotes the exponential function. (45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all. A) sin(x + y) = sin(x)cos(y) + cos(x)sin(y) and. Web start with the definitions of the hyperbolic sine and cosine functions:
Eit = Cos T + I.
Web spring 2003 notes on the complex exponential and sine functions (x1.5) i. If μ r then eiμ def = cos μ + i sin μ. Web solving this linear system in sine and cosine, one can express them in terms of the exponential function: Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions.
Sin X = E I X − E − I X 2 I Cos X = E I X + E − I X 2.
Web using the exponential forms of cos(theta) and sin(theta) given in (3.11a, b), prove the following trigonometric identities: Web hyperbolic functions in mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions, but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circle. Sinz = exp(iz) − exp( − iz) 2i. Web according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and sin(t) via the following inspired definition:
What Is Going On, Is That Electrical Engineers Tend To Ignore The Fact That One Needs To Add Or Subtract The Complex.
E jx = cos (x) + jsin (x) and the exponential representations of sin & cos, which are derived from euler's formula: For any complex number z : Periodicity of the imaginary exponential. I tried using eulers identity to reduce all sine.