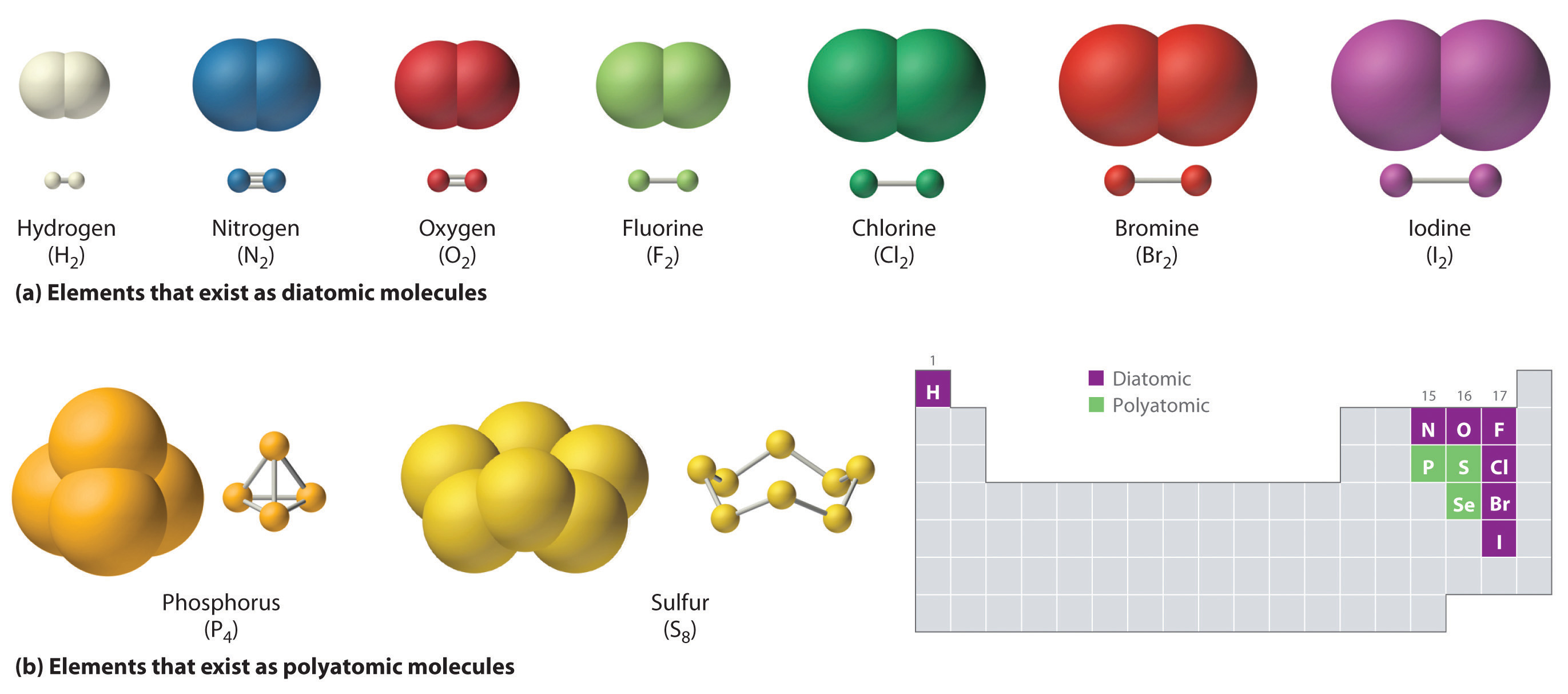
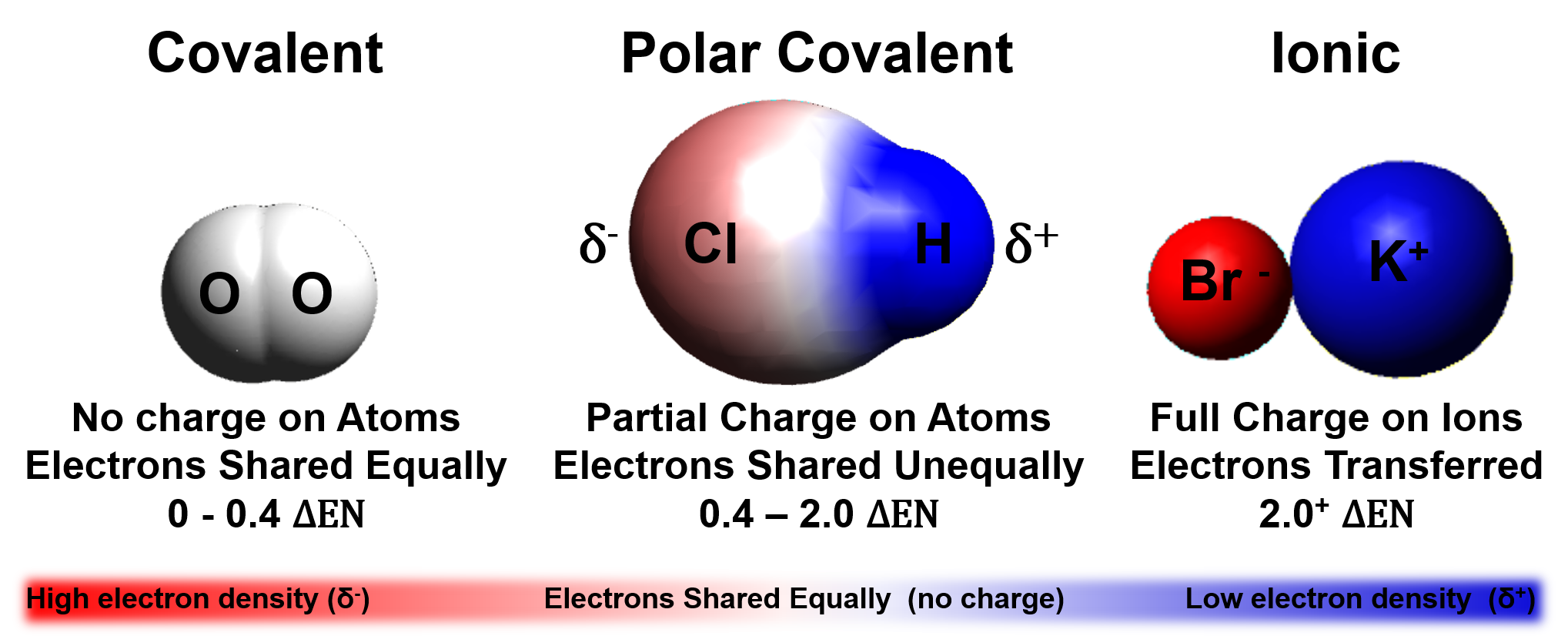
Which Combination Of Atoms Can Form A Polar Covalent Bond
Which Combination Of Atoms Can Form A Polar Covalent Bond - A) hand br ob) hand h c) na and br od) n. A) h and br explanation: The atoms in this bond are xenon (electronegativity 2.6) and fluoride (electronegativity 4.0). The polarity of a bond depends on the electronegativities of the bonded atoms. In a covalent bond, the stability of the bond comes from the shared electrostatic attraction between the two. Web polar covalent bonds are usually formed between two nonmetal atoms having different electronegativities. Web some compounds contain both covalent and ionic bonds. Web non polar covalent bond is defined as type of chemical bond with equal sharing of the bond electron rises when the electronegativity of the two atoms are equal. Web covalent bonds are also affected by the electronegativity of the connected atoms which determines the chemical polarity of the bond. Only h and br form polar covalent bond.
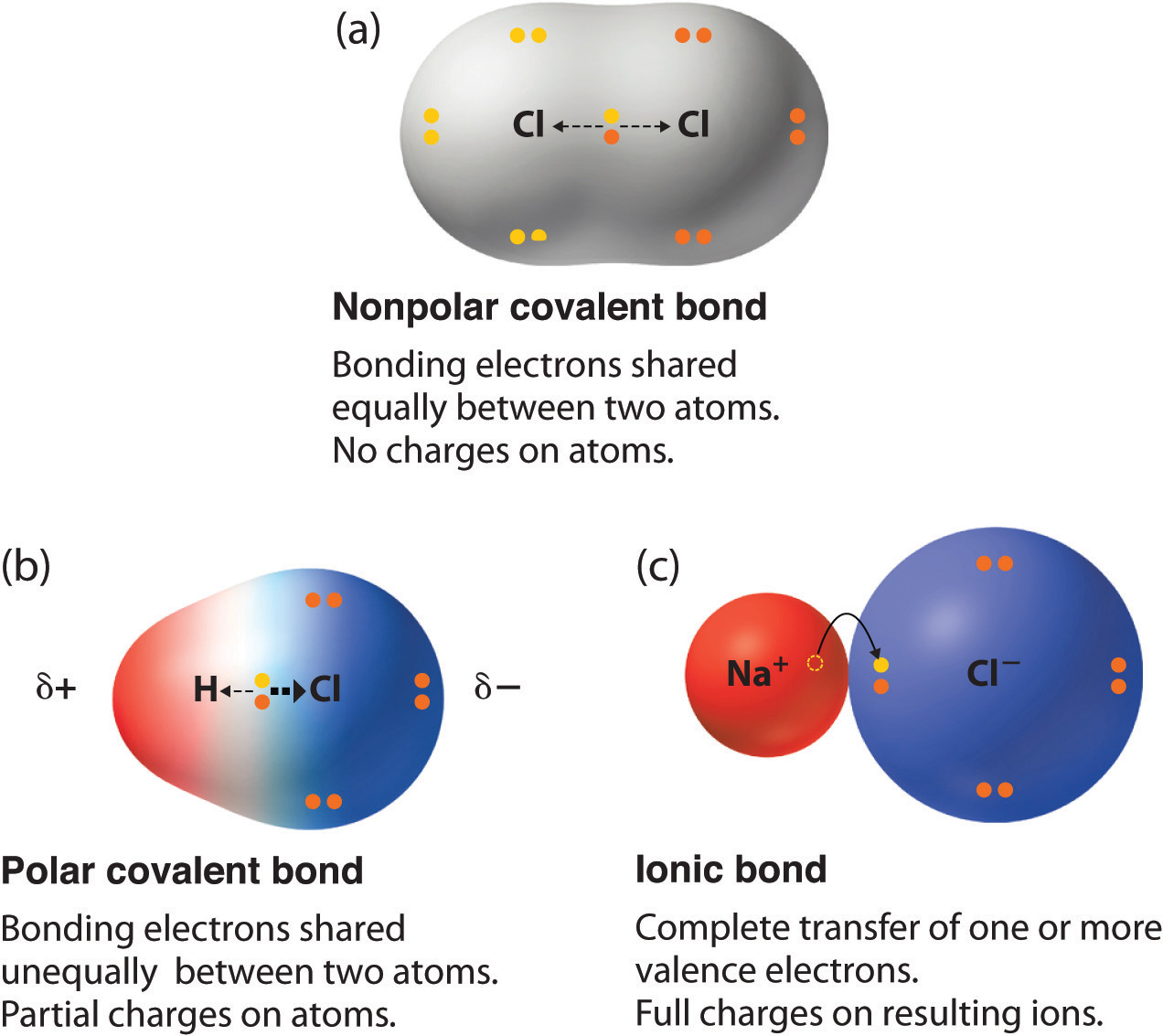
Web non polar covalent bond is defined as type of chemical bond with equal sharing of the bond electron rises when the electronegativity of the two atoms are equal. Web which combination of atoms can form a polar covalent bond? A) hand br ob) hand h c) na and br od) n. The polarity of a bond depends on the electronegativities of the bonded atoms. The atoms in this bond are xenon (electronegativity 2.6) and fluoride (electronegativity 4.0). Web covalent bonds are also affected by the electronegativity of the connected atoms which determines the chemical polarity of the bond. Web 1)molecular compounds where in atoms are joined by covalent bonds. 2) ionic compounds where atoms are joined by ionic bond. Web bonds between carbon and other elements such as oxygen and nitrogen are polar. A) h and br explanation:
Which molecule contains a non polar covalent bond? Which type of bond is present. Web what kind of bond is formed when two atoms share electrons to form a molecule? Web covalent bonds in which the sharing of the electron pair is unequal, with the electrons spending more time around the more nonmetallic atom, are called polar covalent. Web some compounds contain both covalent and ionic bonds. The common factors that affect the conjugate base's stability are 1) the size and. A h and h b h and f c n and n d na and f medium solution verified by toppr correct option is b) answer= h. Web advanced physics advanced physics questions and answers which combination of atoms can form a polar covalent bond? Web the acid that forms the more stable conjugate base will be the stronger acid. A) h and br explanation:
What Is a Polar Bond? Definition and Examples
A) h and br explanation: Web covalent bonds in which the sharing of the electron pair is unequal, with the electrons spending more time around the more nonmetallic atom, are called polar covalent. Only h and br form polar covalent bond. Let us consider a and b in which them is electronegativity difference. Web this creates a spectrum of polarity,.
Covalent Bonds Biology for NonMajors I
Web non polar covalent bond is defined as type of chemical bond with equal sharing of the bond electron rises when the electronegativity of the two atoms are equal. The polarity of a bond depends on the electronegativities of the bonded atoms. Two atoms with equal electronegativity will. The common factors that affect the conjugate base's stability are 1) the.
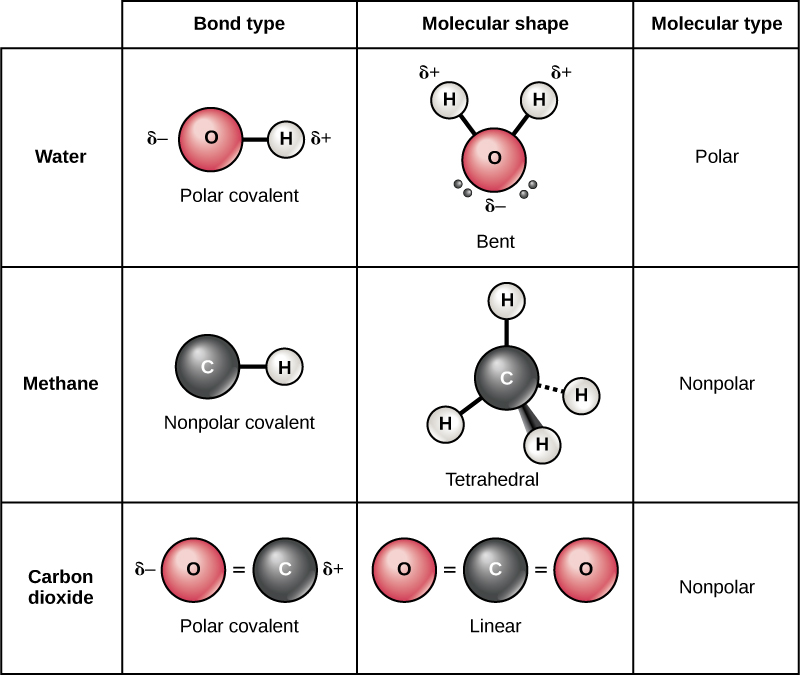
This figure shows the structure of a water molecule. The top panel
Web covalent bonds are also affected by the electronegativity of the connected atoms which determines the chemical polarity of the bond. Web what kind of bond is formed when two atoms share electrons to form a molecule? A h and h b h and f c n and n d na and f medium solution verified by toppr correct option.
2.2 Chemical Bonds Anatomy & Physiology
A) hand br ob) hand h c) na and br od) n. This is due to one of the elements having a higher electronegativity than the. A) h and br explanation: The polarity of a bond depends on the electronegativities of the bonded atoms. Web advanced physics advanced physics questions and answers which combination of atoms can form a polar.
Polar Covalent Bond Definitions, Types and Examples
A) hand br ob) hand h c) na and br od) n. A) h and br explanation: Web a polar covalent bond is a bond formed when a shared pair of electrons are not shared equally. Web which combination of atoms can form a polar covalent bond? Web what kind of bond is formed when two atoms share electrons to.
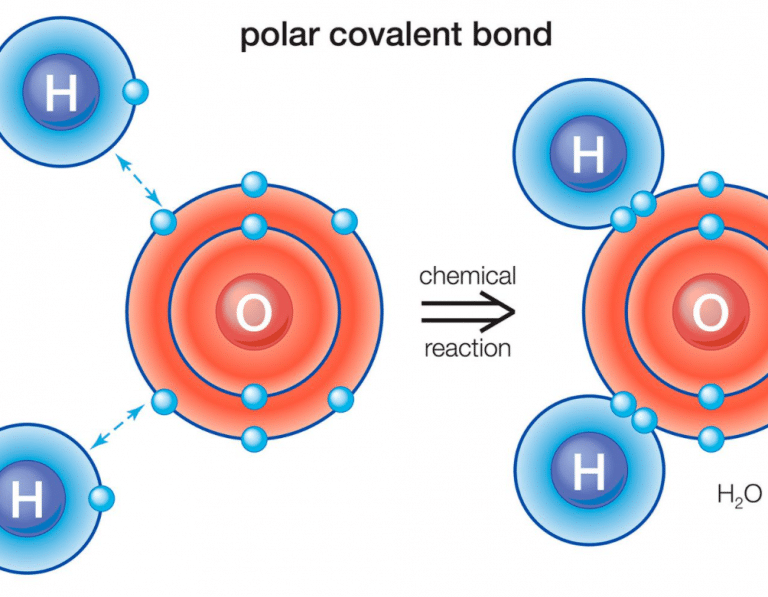
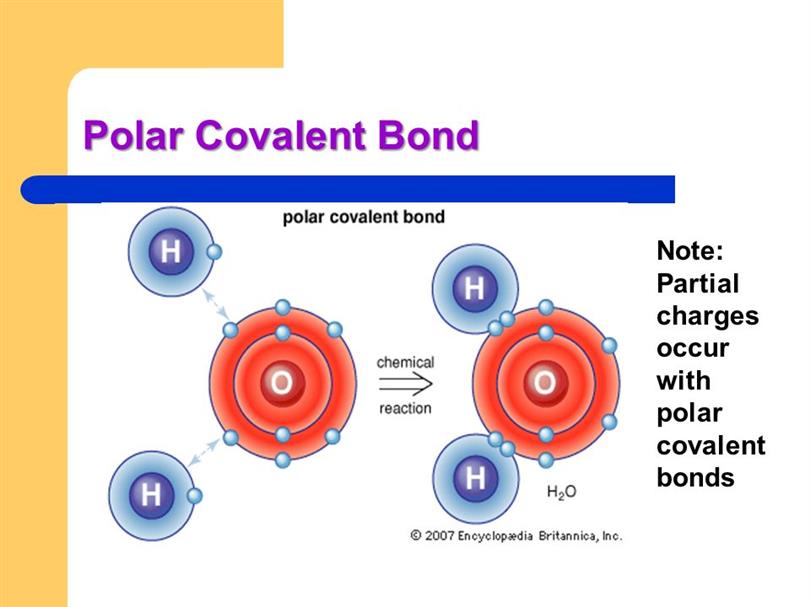
How does a polar bond differ from a covalent bond
The atoms in this bond are xenon (electronegativity 2.6) and fluoride (electronegativity 4.0). Web it takes two electrons to make a covalent bond, one from each bonding atom. Web non polar covalent bond is defined as type of chemical bond with equal sharing of the bond electron rises when the electronegativity of the two atoms are equal. Web some compounds.
Chapter 5.6 Properties of Polar Covalent Bonds Chemistry LibreTexts
Web some compounds contain both covalent and ionic bonds. Web which combination of atoms can form a polar covalent bond? Web a covalent bond is formed when two atoms share electron pairs. This is due to one of the elements having a higher electronegativity than the. Web the acid that forms the more stable conjugate base will be the stronger.
CH150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds Chemistry
Web non polar covalent bond is defined as type of chemical bond with equal sharing of the bond electron rises when the electronegativity of the two atoms are equal. Let us consider a and b in which them is electronegativity difference. Web bonds between carbon and other elements such as oxygen and nitrogen are polar. Web covalent bonds are also.
Ch4 Polar Or Nonpolar Covalent Bond Which statement explains why a
In a covalent bond, the stability of the bond comes from the shared electrostatic attraction between the two. Web bonds between carbon and other elements such as oxygen and nitrogen are polar. Web the acid that forms the more stable conjugate base will be the stronger acid. Web this creates a spectrum of polarity, with ionic (polar) at one extreme,.
Building the World Be Prepared! Everything you should know for 1st
Web advanced physics advanced physics questions and answers which combination of atoms can form a polar covalent bond? Web some compounds contain both covalent and ionic bonds. Web a polar covalent bond is a bond formed when a shared pair of electrons are not shared equally. This is due to one of the elements having a higher electronegativity than the..
A H And H B H And F C N And N D Na And F Medium Solution Verified By Toppr Correct Option Is B) Answer= H.
Web this creates a spectrum of polarity, with ionic (polar) at one extreme, covalent (nonpolar) at another, and polar covalent in the middle. Only h and br form polar covalent bond. Web covalent bonds in which the sharing of the electron pair is unequal, with the electrons spending more time around the more nonmetallic atom, are called polar covalent. Web 1)molecular compounds where in atoms are joined by covalent bonds.
Web What Kind Of Bond Is Formed When Two Atoms Share Electrons To Form A Molecule?
In a covalent bond, the stability of the bond comes from the shared electrostatic attraction between the two. The atoms in this bond are xenon (electronegativity 2.6) and fluoride (electronegativity 4.0). Web which combination of atoms can form a polar covalent bond? A) hand br ob) hand h c) na and br od) n.
Let Us Consider A And B In Which Them Is Electronegativity Difference.
Web it takes two electrons to make a covalent bond, one from each bonding atom. Web some compounds contain both covalent and ionic bonds. Web a polar covalent bond is a bond formed when a shared pair of electrons are not shared equally. Web a covalent bond is formed when two atoms share electron pairs.
2) Ionic Compounds Where Atoms Are Joined By Ionic Bond.
Web advanced physics advanced physics questions and answers which combination of atoms can form a polar covalent bond? Web bonds between carbon and other elements such as oxygen and nitrogen are polar. Which molecule contains a non polar covalent bond? Web the acid that forms the more stable conjugate base will be the stronger acid.
/PolarConvalentBond-58a715be3df78c345b77b57d.jpg)