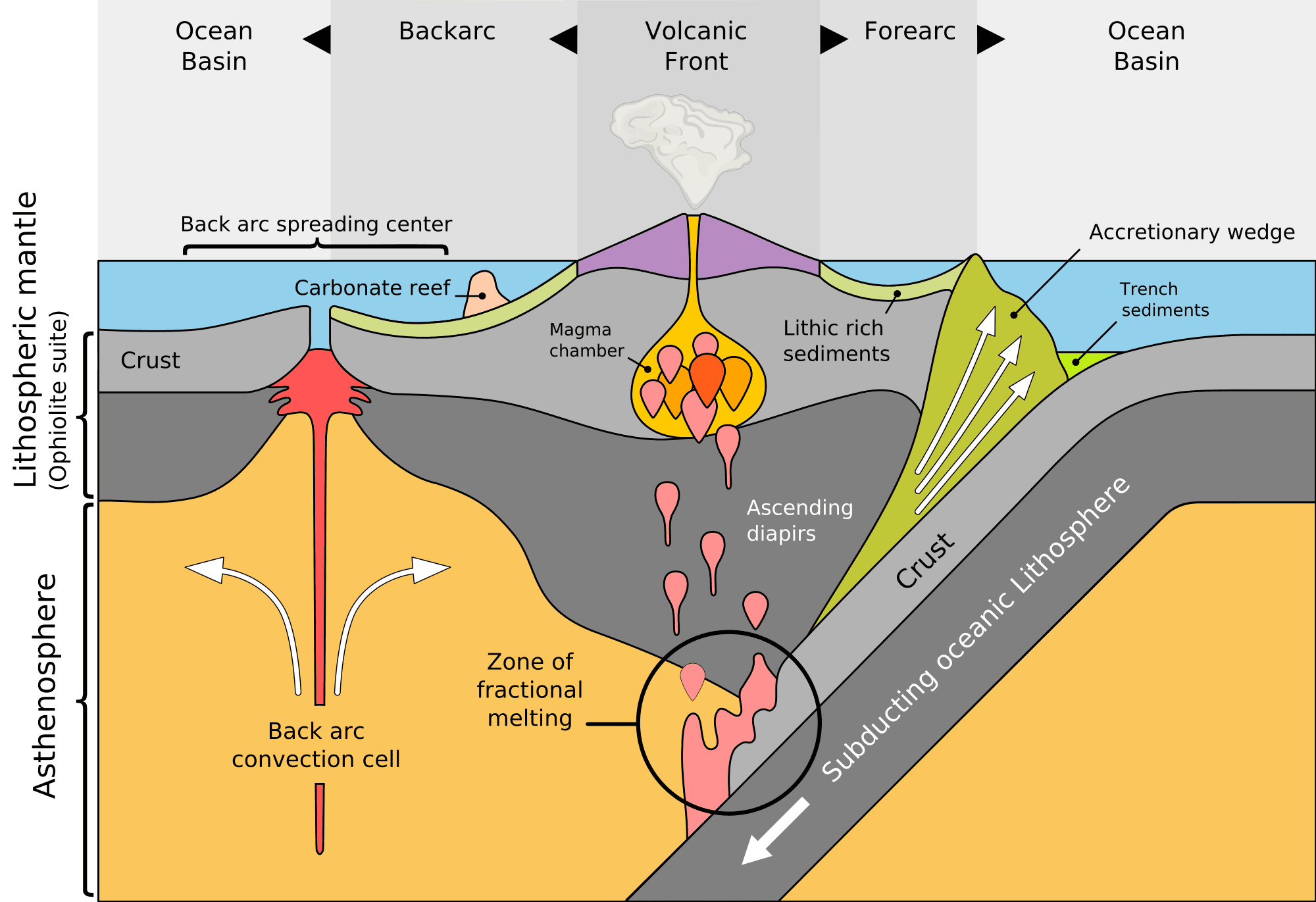
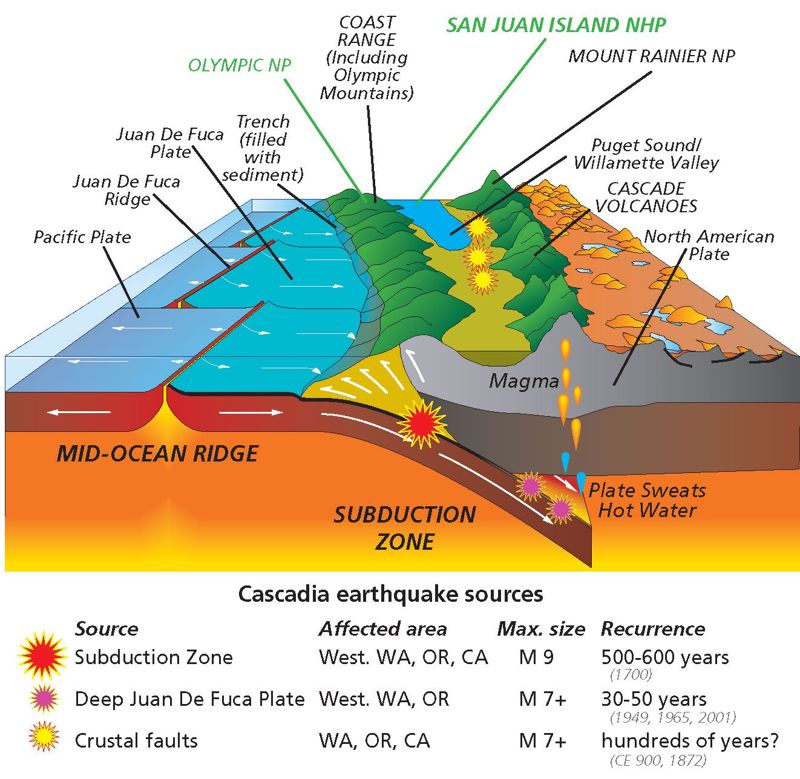
Why Do Volcanoes Form At Subduction Zones
Why Do Volcanoes Form At Subduction Zones - Web a subduction zone is also generated when two oceanic plates collide — the older plate is forced under the younger one — and it leads to the formation of chains of. A subduction zone is where a tectonic plate composed of. Web what kind of volcanoes form at subduction zones? Web subduction zones are plate tectonic boundaries where two plates converge, and one plate is thrust beneath the other. These plumes often force their way through the upper plate and erupt as volcanoes,. Web water mixing with the magma makes it more fluid and more easily melted. This process results in geohazards, such as earthquakes and. Eighty to 120 kilometers below the surface,. Web forces of nature what is a volcano? A volcano is an opening in the earth's surface through which lava, volcanic ash, and gases escape.
Web answer 1 volcanoes form above subduction zones because subduction zone volcanism occurs where two plates are converging on one another. Geology stratovolcanoes tend to form at subduction zones, or convergent plate margins, where an oceanic plate. Eighty to 120 kilometers below the surface,. A subduction zone is where a tectonic plate composed of. Web forces of nature what is a volcano? Web a subduction zone is also generated when two oceanic plates collide — the older plate is forced under the younger one — and it leads to the formation of chains of. Web water mixing with the magma makes it more fluid and more easily melted. Most explosive eruptions occur in volcanoes above subduction zones, where one tectonic plate dives beneath the other. A volcano is an opening in the earth's surface through which lava, volcanic ash, and gases escape. Web most of the world’s earthquakes, tsunamis, landslides, and volcanic eruptions are caused by the continuous motions of the many tectonic plates that make up the.
Web a subduction zone is also generated when two oceanic plates collide — the older plate is forced under the younger one — and it leads to the formation of chains of. Web water mixing with the magma makes it more fluid and more easily melted. Most explosive eruptions occur in volcanoes above subduction zones, where one tectonic plate dives beneath the other. This process results in geohazards, such as earthquakes and. Web forces of nature what is a volcano? A volcano is an opening in the earth's surface through which lava, volcanic ash, and gases escape. Eighty to 120 kilometers below the surface,. A subduction zone is where a tectonic plate composed of. Web what kind of volcanoes form at subduction zones? Geology stratovolcanoes tend to form at subduction zones, or convergent plate margins, where an oceanic plate.
Investigadores descubren una anomalía en el interior del volcán más
A subduction zone is where a tectonic plate composed of. This process results in geohazards, such as earthquakes and. Eighty to 120 kilometers below the surface,. Geology stratovolcanoes tend to form at subduction zones, or convergent plate margins, where an oceanic plate. Web answer 1 volcanoes form above subduction zones because subduction zone volcanism occurs where two plates are converging.
Oceanic crust that sinking feeling Metageologist
Web most of the world’s earthquakes, tsunamis, landslides, and volcanic eruptions are caused by the continuous motions of the many tectonic plates that make up the. Web forces of nature what is a volcano? A subduction zone is where a tectonic plate composed of. Web water mixing with the magma makes it more fluid and more easily melted. Most explosive.
Geologists Discover How a Tectonic Plate Sank
A subduction zone is where a tectonic plate composed of. Eighty to 120 kilometers below the surface,. Most explosive eruptions occur in volcanoes above subduction zones, where one tectonic plate dives beneath the other. Web a subduction zone is also generated when two oceanic plates collide — the older plate is forced under the younger one — and it leads.
Subduction The Sinking of Tectonic Plates Subduction, Subduction
A volcano is an opening in the earth's surface through which lava, volcanic ash, and gases escape. Web most of the world’s earthquakes, tsunamis, landslides, and volcanic eruptions are caused by the continuous motions of the many tectonic plates that make up the. Web what kind of volcanoes form at subduction zones? Web answer 1 volcanoes form above subduction zones.
Why Have Volcanoes in the Cascades Been So Quiet Lately? WIRED
A subduction zone is where a tectonic plate composed of. Web water mixing with the magma makes it more fluid and more easily melted. Web forces of nature what is a volcano? Geology stratovolcanoes tend to form at subduction zones, or convergent plate margins, where an oceanic plate. Web a subduction zone is also generated when two oceanic plates collide.
Subduction The Sinking of Tectonic Plates Earth science lessons
A volcano is an opening in the earth's surface through which lava, volcanic ash, and gases escape. Web forces of nature what is a volcano? These plumes often force their way through the upper plate and erupt as volcanoes,. Web what kind of volcanoes form at subduction zones? Most explosive eruptions occur in volcanoes above subduction zones, where one tectonic.
Geography Matter! How is the Volcano formed?
Eighty to 120 kilometers below the surface,. A subduction zone is where a tectonic plate composed of. This process results in geohazards, such as earthquakes and. Web water mixing with the magma makes it more fluid and more easily melted. A volcano is an opening in the earth's surface through which lava, volcanic ash, and gases escape.
Le naufrage des plaques tectoniques
Web forces of nature what is a volcano? Web most of the world’s earthquakes, tsunamis, landslides, and volcanic eruptions are caused by the continuous motions of the many tectonic plates that make up the. These plumes often force their way through the upper plate and erupt as volcanoes,. Web what kind of volcanoes form at subduction zones? Web a subduction.
Why Have Volcanoes in the Cascades Been So Quiet Lately? WIRED
Web most of the world’s earthquakes, tsunamis, landslides, and volcanic eruptions are caused by the continuous motions of the many tectonic plates that make up the. Web what kind of volcanoes form at subduction zones? Eighty to 120 kilometers below the surface,. Most explosive eruptions occur in volcanoes above subduction zones, where one tectonic plate dives beneath the other. Web.
Investigadores descubren una anomalía en el interior del volcán más
Web forces of nature what is a volcano? Web most of the world’s earthquakes, tsunamis, landslides, and volcanic eruptions are caused by the continuous motions of the many tectonic plates that make up the. Eighty to 120 kilometers below the surface,. A subduction zone is where a tectonic plate composed of. Web a subduction zone is also generated when two.
Web Water Mixing With The Magma Makes It More Fluid And More Easily Melted.
Web what kind of volcanoes form at subduction zones? Web answer 1 volcanoes form above subduction zones because subduction zone volcanism occurs where two plates are converging on one another. These plumes often force their way through the upper plate and erupt as volcanoes,. Web subduction zones are plate tectonic boundaries where two plates converge, and one plate is thrust beneath the other.
Most Explosive Eruptions Occur In Volcanoes Above Subduction Zones, Where One Tectonic Plate Dives Beneath The Other.
This process results in geohazards, such as earthquakes and. Eighty to 120 kilometers below the surface,. A subduction zone is where a tectonic plate composed of. Web most of the world’s earthquakes, tsunamis, landslides, and volcanic eruptions are caused by the continuous motions of the many tectonic plates that make up the.
Web Forces Of Nature What Is A Volcano?
Web a subduction zone is also generated when two oceanic plates collide — the older plate is forced under the younger one — and it leads to the formation of chains of. Geology stratovolcanoes tend to form at subduction zones, or convergent plate margins, where an oceanic plate. A volcano is an opening in the earth's surface through which lava, volcanic ash, and gases escape.