Why Does A Meniscus Form
Why Does A Meniscus Form - A torn meniscus can result from any activity that causes you to forcefully twist or rotate your knee, such as aggressive pivoting or sudden stops and turns. A meniscus is a curved liquid surface that results from the interplay of adhesion (the liquid's attraction to its container) and cohesion (the liquid's attraction to itself). Web the one on the inside of the knee is the medial meniscus and the one on the outside is the lateral meniscus. Without the meniscus, you wouldn't. Sometimes, degeneration from arthritis causes a tear, even without a knee injury. People whose cartilage wears down (due to age or arthritis) can tear a meniscus from a motion as simple as stepping on an uneven surface. This band forms a concave support pad for the thigh bone to rest on. With water, you can think of it as when water sticks to the inside of a glass. Their biochemical composition and multilayered structure make them ideal for converting compressive forces to tensile forces in addition to improving joint congruity and providing. Web capillary action and why we see a meniscus.
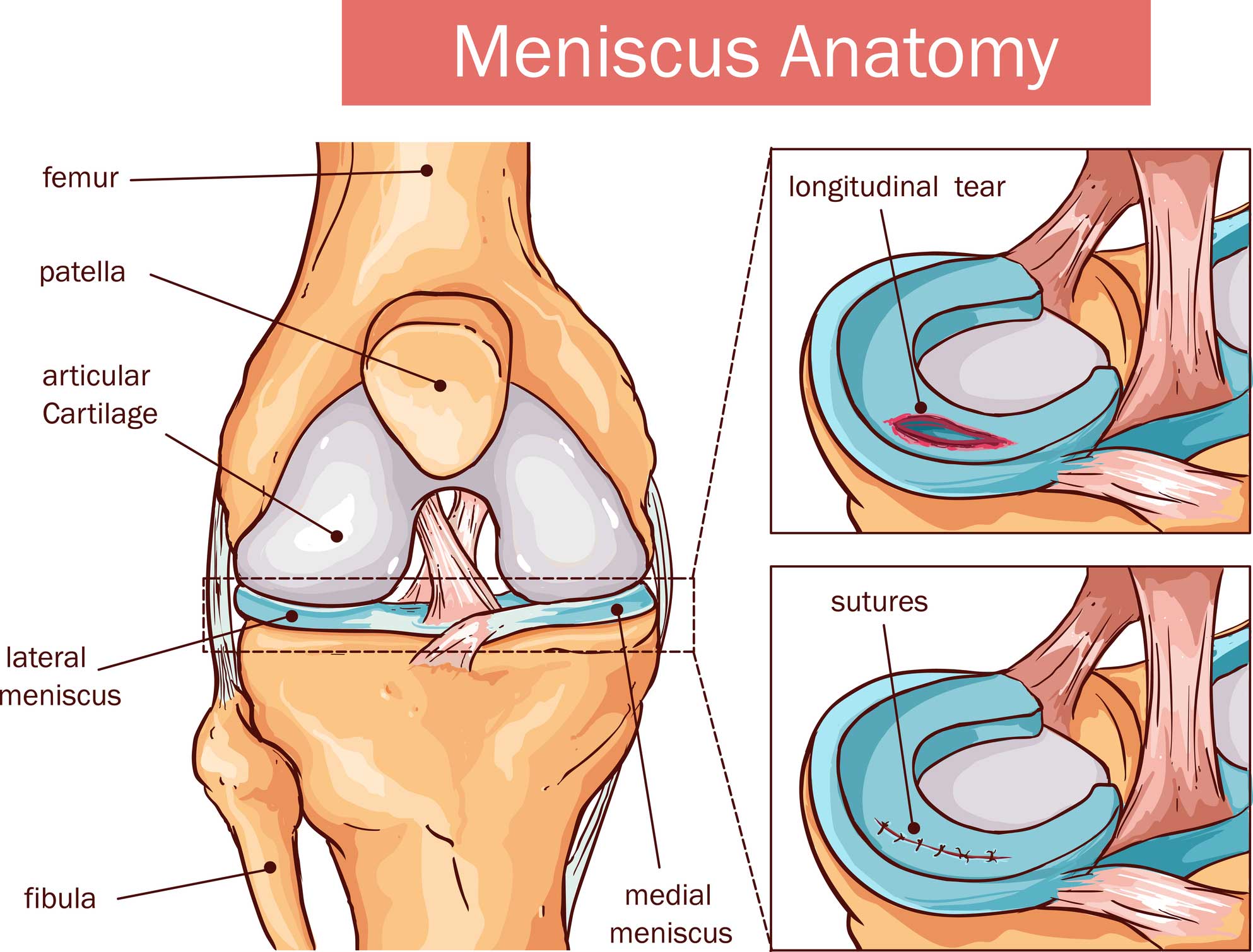
Even kneeling, deep squatting or lifting something heavy can sometimes lead to a. People whose cartilage wears down (due to age or arthritis) can tear a meniscus from a motion as simple as stepping on an uneven surface. Web meniscus tears usually take place when an athlete twists or turns their upper leg while their foot is planted and their knee is bent. These multiple and complex functions require a specialized form. Their biochemical composition and multilayered structure make them ideal for converting compressive forces to tensile forces in addition to improving joint congruity and providing. Sometimes, degeneration from arthritis causes a tear, even without a knee injury. Each meniscus is smooth, flexible, and rubbery, and acts to provide both stability and shock absorbing protection to the precious knee cartilage lining the joint, also known as the hyaline cartilage. A torn meniscus can result from any activity that causes you to forcefully twist or rotate your knee, such as aggressive pivoting or sudden stops and turns. A discoid meniscus is more likely to tear and commonly presents in childhood. Web the one on the inside of the knee is the medial meniscus and the one on the outside is the lateral meniscus.
Web the meniscus withstands many different forces such as shear, tension, and compression. With water, you can think of it as when water sticks to the inside of a glass. A torn meniscus can result from any activity that causes you to forcefully twist or rotate your knee, such as aggressive pivoting or sudden stops and turns. Without the meniscus, you wouldn't. A discoid meniscus is more likely to tear and commonly presents in childhood. Web a meniscus is formed because the adhesive and cohesive forces don't balance each other perfectly,so there can be extra pull/push due to the force between the surface of the container and the fluid, which forms a meniscus. Sometimes, degeneration from arthritis causes a tear, even without a knee injury. Web the tear frequently occurs while playing sports. This band forms a concave support pad for the thigh bone to rest on. Their biochemical composition and multilayered structure make them ideal for converting compressive forces to tensile forces in addition to improving joint congruity and providing.
Meniscus Tears Florida Orthopaedic Institute
Web meniscus form and function. Adhesion is responsible for a meniscus and this has to do in part with water's fairly high surface tension. A torn meniscus can result from any activity that causes you to forcefully twist or rotate your knee, such as aggressive pivoting or sudden stops and turns. Web a meniscus is formed because the adhesive and.
Meniscus Injuries Part 1 Surgery "NOT Required"
These multiple and complex functions require a specialized form. This band forms a concave support pad for the thigh bone to rest on. Each meniscus is smooth, flexible, and rubbery, and acts to provide both stability and shock absorbing protection to the precious knee cartilage lining the joint, also known as the hyaline cartilage. Adhesion is responsible for a meniscus.
What Does a Torn Meniscus (Meniscus Tear) Feel Like? — THE SPORTS
Sometimes, degeneration from arthritis causes a tear, even without a knee injury. Web the one on the inside of the knee is the medial meniscus and the one on the outside is the lateral meniscus. Web the meniscus withstands many different forces such as shear, tension, and compression. Adhesion is responsible for a meniscus and this has to do in.
How Meniscus Tears Affect Athletic Performance MASS4D® Foot Orthotics
Web a meniscus is a curve in the surface of a molecular substance (water, of course) when it touches another material. Even kneeling, deep squatting or lifting something heavy can sometimes lead to a. The menisci are 2 fibrocartilaginous crescents anchored via bony and ligamentous attachments to surrounding structures. Sometimes, degeneration from arthritis causes a tear, even without a knee.
Failure of meniscus repairs Dr. David Geier Sports Medicine Simplified
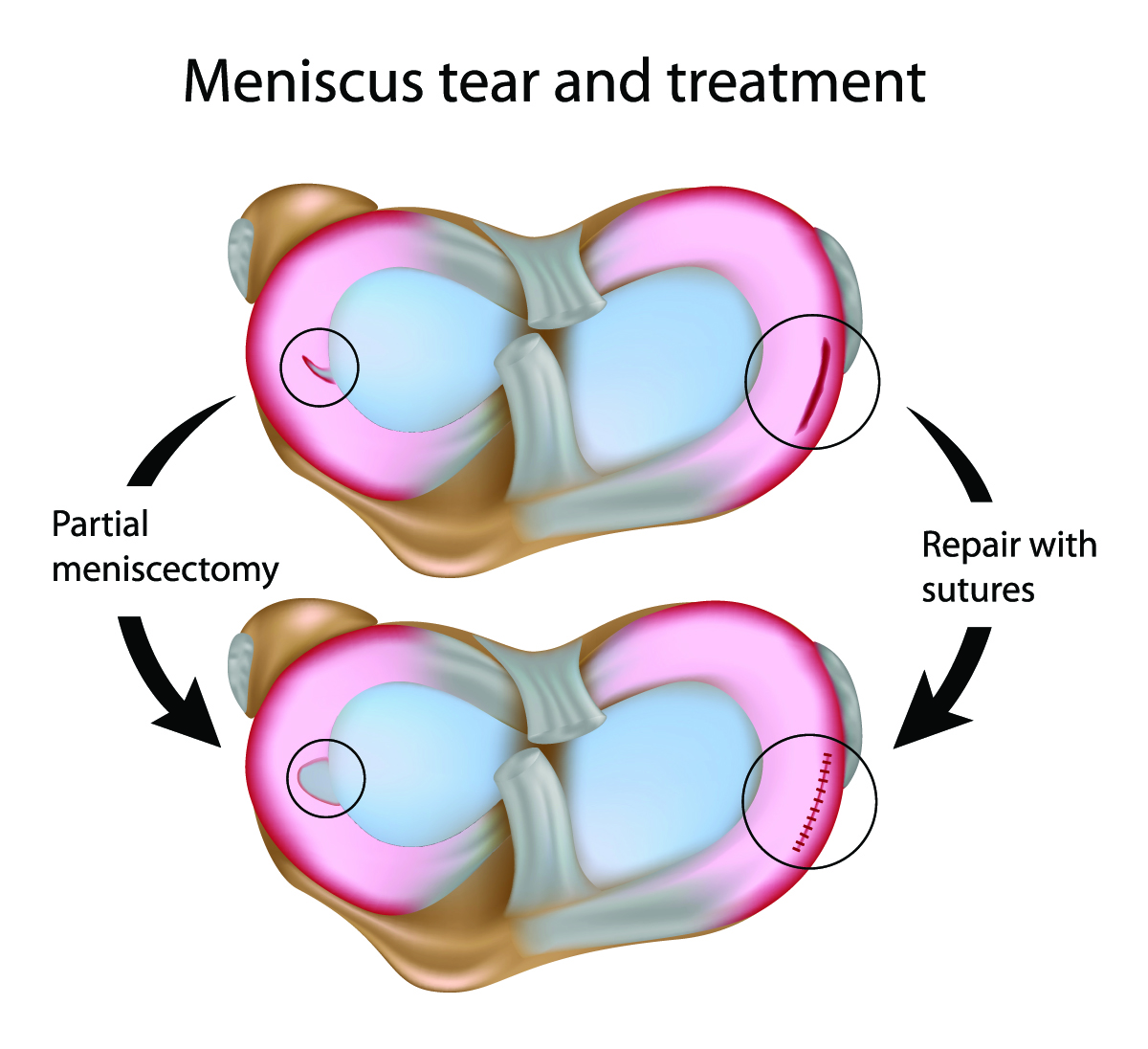
This band forms a concave support pad for the thigh bone to rest on. Web a meniscus is formed because the adhesive and cohesive forces don't balance each other perfectly,so there can be extra pull/push due to the force between the surface of the container and the fluid, which forms a meniscus. People whose cartilage wears down (due to age.
The Injury Zone Meniscus Tear, What are my options?
Sometimes, degeneration from arthritis causes a tear, even without a knee injury. Web the tear frequently occurs while playing sports. These multiple and complex functions require a specialized form. A discoid meniscus is more likely to tear and commonly presents in childhood. People whose cartilage wears down (due to age or arthritis) can tear a meniscus from a motion as.
NFL Week 14 Injury Report How a Torn Meniscus Can Change Your Life
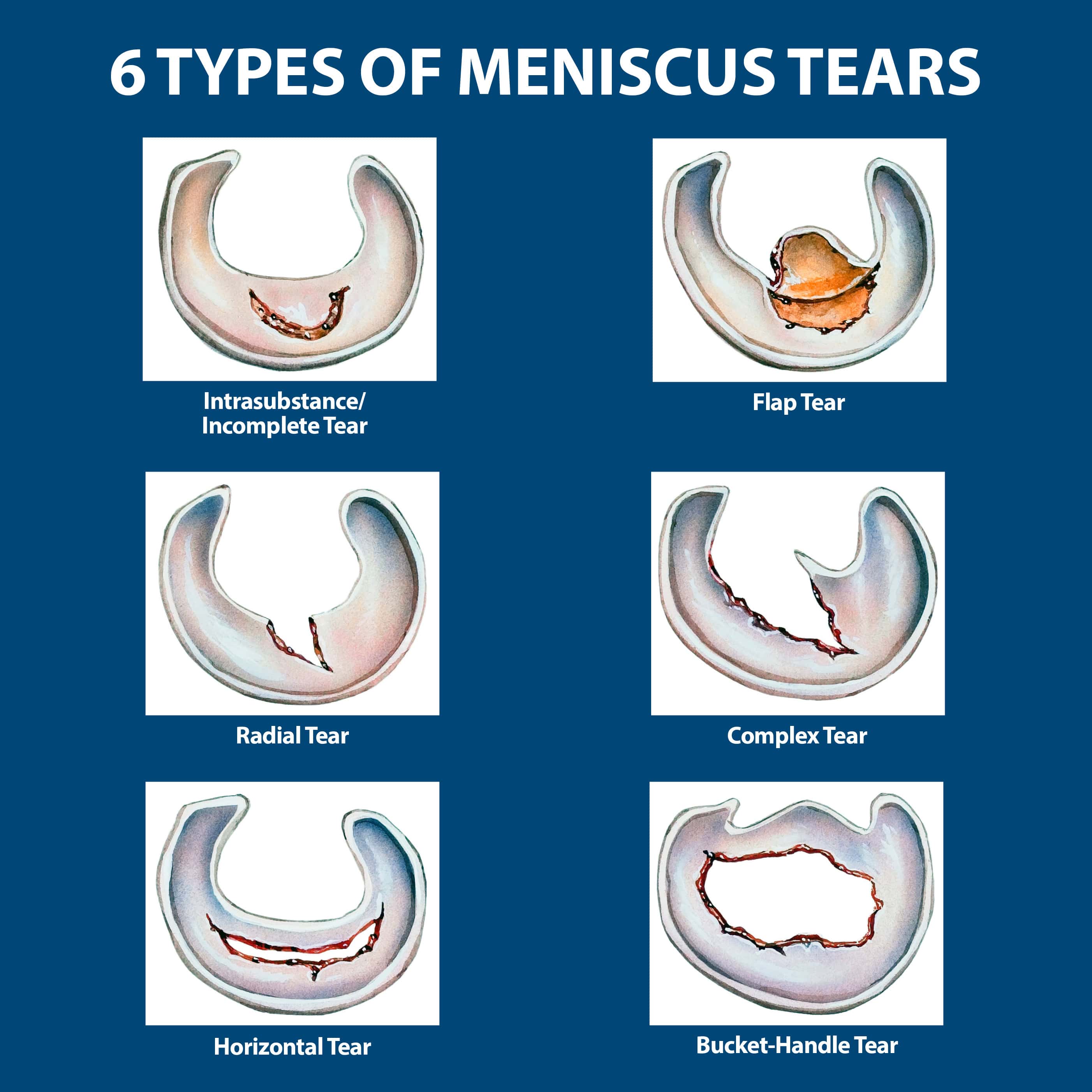
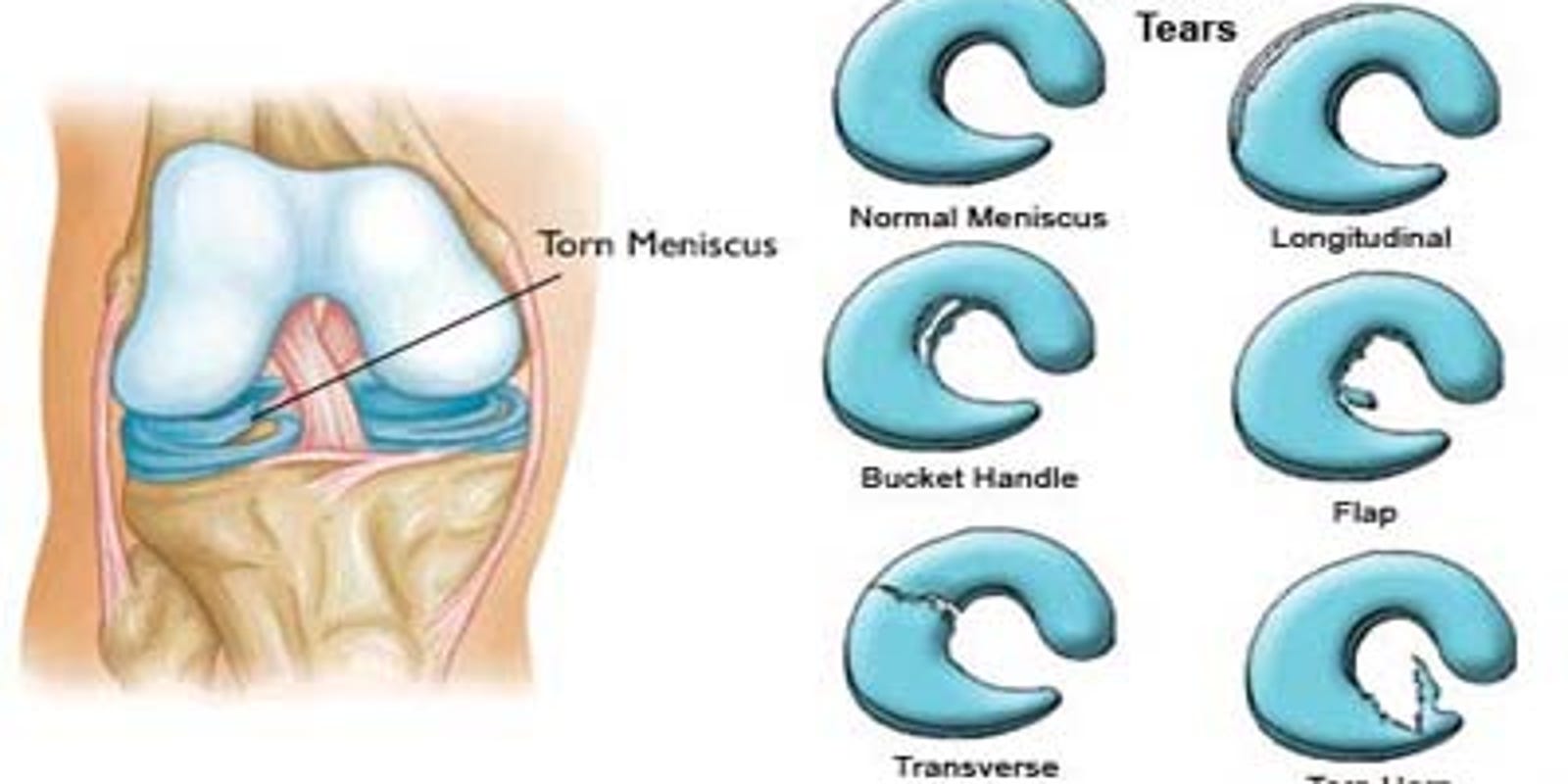
A discoid meniscus is more likely to tear and commonly presents in childhood. The menisci are 2 fibrocartilaginous crescents anchored via bony and ligamentous attachments to surrounding structures. This band forms a concave support pad for the thigh bone to rest on. Without the meniscus, you wouldn't. Occasionally menisci can develop as a block or disk shape, which is called.
Meniscus tears of the knee and what it means for you. Arana Hills
Adhesion is responsible for a meniscus and this has to do in part with water's fairly high surface tension. Sometimes, degeneration from arthritis causes a tear, even without a knee injury. Web a meniscus is a curve in the surface of a molecular substance (water, of course) when it touches another material. With water, you can think of it as.
Meniscus Form & Function YouTube
Occasionally menisci can develop as a block or disk shape, which is called a discoid meniscus. A discoid meniscus is more likely to tear and commonly presents in childhood. Each meniscus is smooth, flexible, and rubbery, and acts to provide both stability and shock absorbing protection to the precious knee cartilage lining the joint, also known as the hyaline cartilage..
Water Pouring Why does water stick to glass when pouring?
A torn meniscus can result from any activity that causes you to forcefully twist or rotate your knee, such as aggressive pivoting or sudden stops and turns. Sometimes, degeneration from arthritis causes a tear, even without a knee injury. Web meniscus tears usually take place when an athlete twists or turns their upper leg while their foot is planted and.
Web A Meniscus Is Formed Because The Adhesive And Cohesive Forces Don't Balance Each Other Perfectly,So There Can Be Extra Pull/Push Due To The Force Between The Surface Of The Container And The Fluid, Which Forms A Meniscus.
A torn meniscus can result from any activity that causes you to forcefully twist or rotate your knee, such as aggressive pivoting or sudden stops and turns. A discoid meniscus is more likely to tear and commonly presents in childhood. Web the one on the inside of the knee is the medial meniscus and the one on the outside is the lateral meniscus. Even kneeling, deep squatting or lifting something heavy can sometimes lead to a.
Web Meniscus Tears Usually Take Place When An Athlete Twists Or Turns Their Upper Leg While Their Foot Is Planted And Their Knee Is Bent.
Web the meniscus withstands many different forces such as shear, tension, and compression. Their biochemical composition and multilayered structure make them ideal for converting compressive forces to tensile forces in addition to improving joint congruity and providing. Sometimes, degeneration from arthritis causes a tear, even without a knee injury. Web the tear frequently occurs while playing sports.
These Multiple And Complex Functions Require A Specialized Form.
Each meniscus is smooth, flexible, and rubbery, and acts to provide both stability and shock absorbing protection to the precious knee cartilage lining the joint, also known as the hyaline cartilage. Web capillary action and why we see a meniscus. Without the meniscus, you wouldn't. With water, you can think of it as when water sticks to the inside of a glass.
Web A Meniscus Is A Curve In The Surface Of A Molecular Substance (Water, Of Course) When It Touches Another Material.
People whose cartilage wears down (due to age or arthritis) can tear a meniscus from a motion as simple as stepping on an uneven surface. Adhesion is responsible for a meniscus and this has to do in part with water's fairly high surface tension. Web meniscus form and function. A meniscus is a curved liquid surface that results from the interplay of adhesion (the liquid's attraction to its container) and cohesion (the liquid's attraction to itself).