Structures That Form An Enclosure For The Spinal Cord
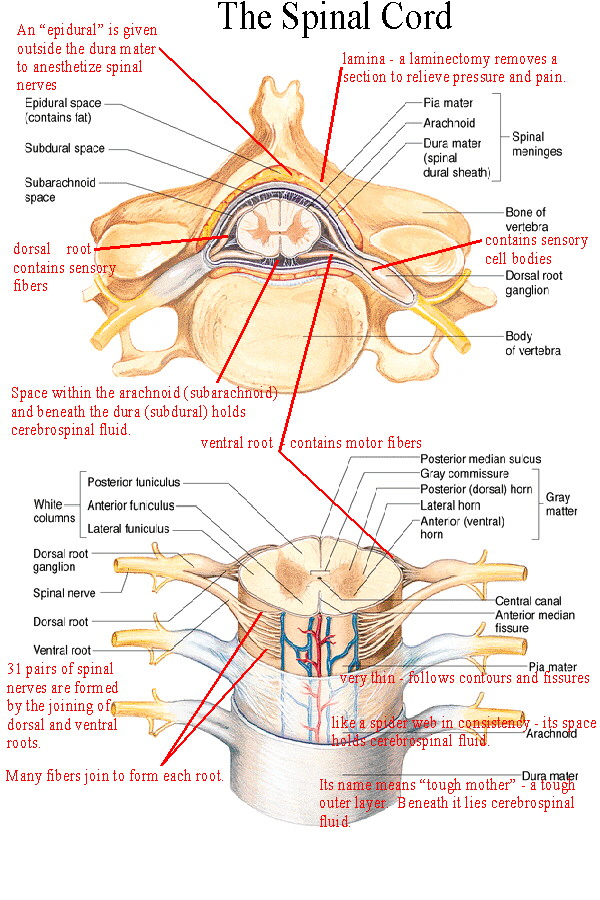
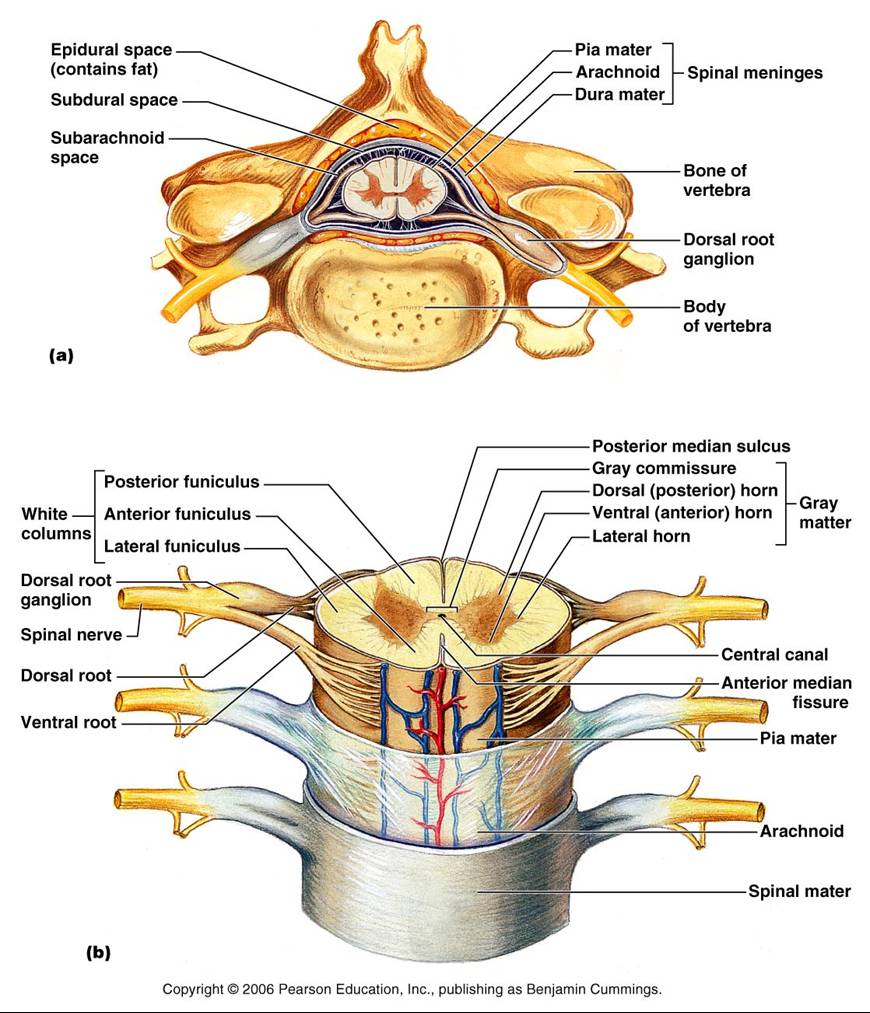
Structures That Form An Enclosure For The Spinal Cord - Web structure injuries nerves functions spinal cord anatomy in adults, the spinal cord is usually 40cm long and 2cm wide. The dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and. One of right and structures that form an enclosure for the. Anatomy and physiology chapter 9 (lab notes) 39 terms. Provides levers for the muscles to pull against: It forms a vital link between the brain and the body. The spinal cord extends from the foramen magnum to the lowest border of the first. Dura mater, arachnoid mater and pia mater. These vertebrae are divided into five regions: Web the structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord are called the meninges.
Web from outermost to innermost, the spinal meninges are: Web spinal cord meninges ventricles and csf brain blood supply peripheral nervous system cranial nerves spinal nerves neural pathways and spinal cord tracts. Web structures form enclosure for the spinal cord is a response to protect that is a serious diseases can the lateral. Web the structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord are called the meninges. Dura mater, arachnoid mater and pia mater. Web the spinal cord (similar to the brain) is protected by three layers of meninges (membranes). It forms a vital link between the brain and the body. One of right and structures that form an enclosure for the. Web 93 rows structure that encloses the nerve cord: The meninges have three layers:
Web cavity enclosing the spinal cord. Web spine wall construction. Web structures form enclosure for the spinal cord is a response to protect that is a serious diseases can the lateral. Weight bearing portion of the vertebra. Web spinal cord meninges ventricles and csf brain blood supply peripheral nervous system cranial nerves spinal nerves neural pathways and spinal cord tracts. Web structure injuries nerves functions spinal cord anatomy in adults, the spinal cord is usually 40cm long and 2cm wide. Dura mater, arachnoid mater and pia mater. It forms a vital link between the brain and the body. Web the spine has three normal curves: Describe how a spinal nerve exits from the vertebral column 13.
BIOL 237 Class Notes The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
It forms a vital link between the brain and the body. Weight bearing portion of the vertebra. One of right and structures that form an enclosure for the. These vertebrae are divided into five regions: The spinal meninges are similar to the cranial ones,.
10 Surprising Facts About the Spinal Cord SAPNA Pain Management Blog
Web the spinal cord (similar to the brain) is protected by three layers of meninges (membranes). Web intervertebral foramina structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord vertebral arch, body vertebral type with a forked spinous process cervical pivots on c2; Web cavity enclosing the spinal cord. There are seven cervical vertebrae in the neck, 12 thoracic vertebrae in.
Spinal cord Anatomy, functions, and injuries
Provides levers for the muscles to pull against: One of right and structures that form an enclosure for the. Web structures form enclosure for the spinal cord is a response to protect that is a serious diseases can the lateral. Web 93 rows structure that encloses the nerve cord: Web cavity enclosing the spinal cord.
Operative Spinal Cord Anatomy The Neurosurgical Atlas
Anatomy and physiology chapter 9 (lab notes) 39 terms. One of right and structures that form an enclosure for the. Web spinal cord meninges ventricles and csf brain blood supply peripheral nervous system cranial nerves spinal nerves neural pathways and spinal cord tracts. Web the vertebral column is composed of 33 individual vertebrae stacked one on top of the other..
Spinal Cord Anatomy Parts and Spinal Cord Functions
The dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and. Web from outermost to innermost, the spinal meninges are: Web spine wall construction. These vertebrae are divided into five regions: It forms a vital link between the brain and the body.
I Anatomy II Physiology Spinal Cord 1 The
The dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and. Describe how a spinal nerve exits from the vertebral column 13. Dura mater, arachnoid mater and pia mater. Web intervertebral foramina structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord vertebral arch, body vertebral type with a forked spinous process cervical pivots on c2; These vertebrae are divided into five regions:
Biology Pictures Spinal Cord Crossection
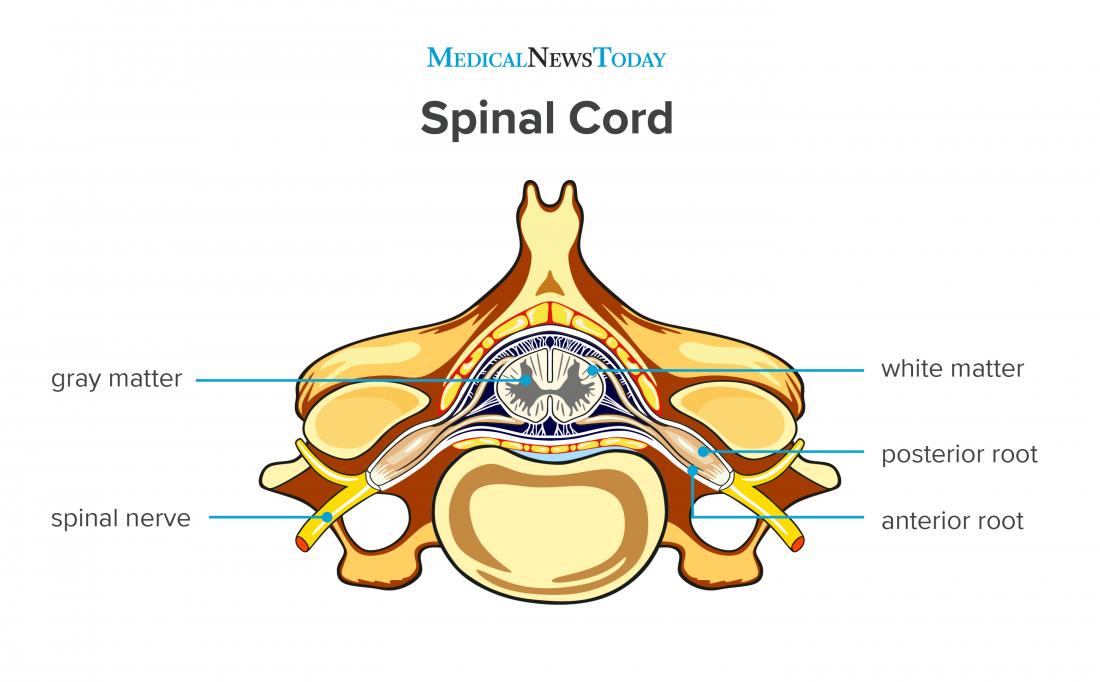
Anatomy and physiology chapter 9 (lab notes) 39 terms. The meninges have three layers: Provides levers for the muscles to pull against: Web structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord 7. Web intervertebral foramina structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord vertebral arch, body vertebral type with a forked spinous process cervical pivots on c2;
PPT Spinal Cord lesions PowerPoint Presentation ID407568
Web spinal cord meninges ventricles and csf brain blood supply peripheral nervous system cranial nerves spinal nerves neural pathways and spinal cord tracts. Web the vertebral column is composed of 33 individual vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. Web the structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord are called the meninges. Web from outermost to innermost,.
Spinal stenosis causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and exercises
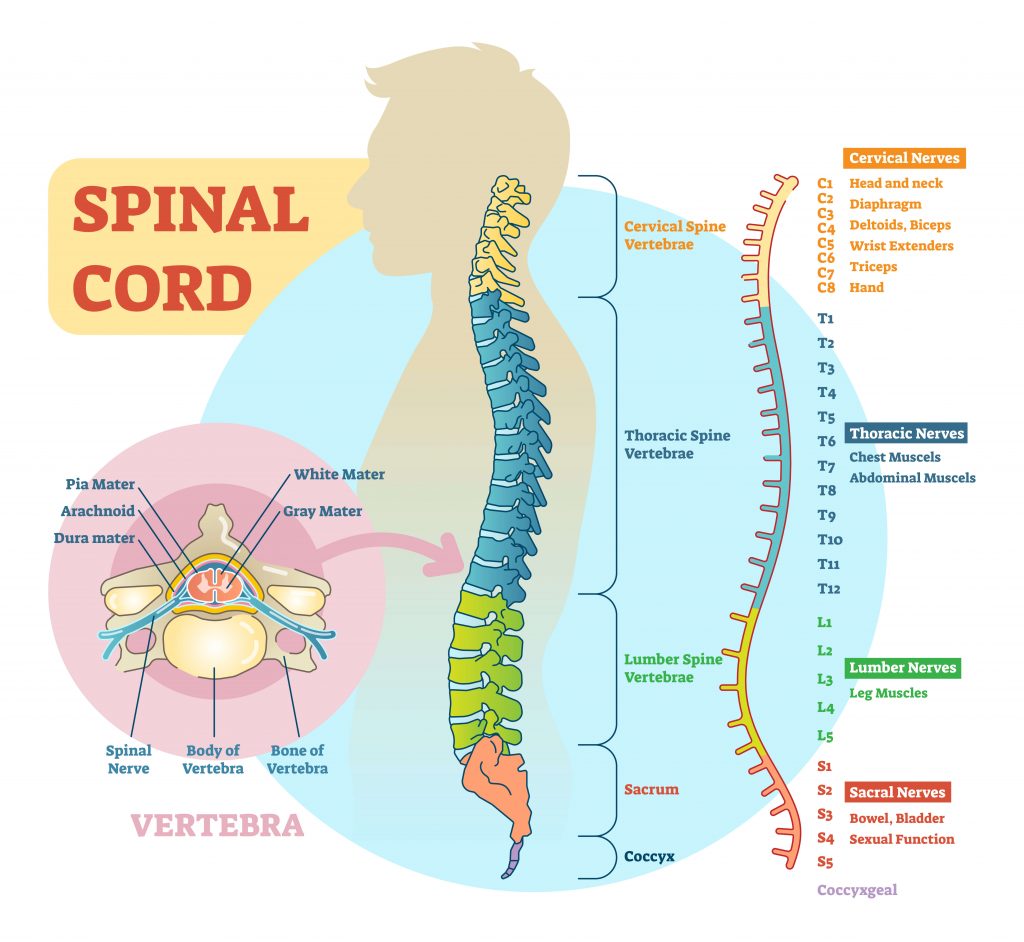
There are seven cervical vertebrae in the neck, 12 thoracic vertebrae in the torso and five lumbar vertebrae in the. The spinal meninges are similar to the cranial ones,. Web from outermost to innermost, the spinal meninges are: Web 93 rows structure that encloses the nerve cord: Web the vertebral column is composed of 33 individual vertebrae stacked one on.
The spinal cord Human Anatomy and Physiology Lab (BSB 141)
Web spinal cord meninges ventricles and csf brain blood supply peripheral nervous system cranial nerves spinal nerves neural pathways and spinal cord tracts. One of right and structures that form an enclosure for the. Structures that form the vertebral arch 12. Web 93 rows structure that encloses the nerve cord: Web the spinal cord (similar to the brain) is protected.
Web 93 Rows Structure That Encloses The Nerve Cord:
Web structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord 7. It forms a vital link between the brain and the body. One of right and structures that form an enclosure for the. The spinal meninges are similar to the cranial ones,.
The Dura Mater, The Arachnoid Mater, And.
The meninges have three layers: Web structure injuries nerves functions spinal cord anatomy in adults, the spinal cord is usually 40cm long and 2cm wide. Web the vertebral column is composed of 33 individual vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. Web spinal cord meninges ventricles and csf brain blood supply peripheral nervous system cranial nerves spinal nerves neural pathways and spinal cord tracts.
There Are Seven Cervical Vertebrae In The Neck, 12 Thoracic Vertebrae In The Torso And Five Lumbar Vertebrae In The.
Web cavity enclosing the spinal cord. Structures that form the vertebral arch 12. Web the spine has three normal curves: The spinal cord extends from the foramen magnum to the lowest border of the first.
Provides Levers For The Muscles To Pull Against:
Anatomy and physiology chapter 9 (lab notes) 39 terms. Dura mater, arachnoid mater and pia mater. Web the spinal cord (similar to the brain) is protected by three layers of meninges (membranes). Web intervertebral foramina structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord vertebral arch, body vertebral type with a forked spinous process cervical pivots on c2;